Contribution of Short-Time Occlusion of the Amblyopic Eye to a Passive Dichoptic Video Treatment for Amblyopia beyond the Critical Period
- PMID: 31558900
- PMCID: PMC6735187
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/6208414
Contribution of Short-Time Occlusion of the Amblyopic Eye to a Passive Dichoptic Video Treatment for Amblyopia beyond the Critical Period
Abstract
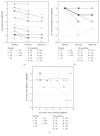
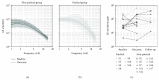
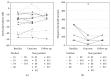
Dichoptic movie viewing has been shown to significantly improve visual acuity in amblyopia in children. Moreover, short-term occlusion of the amblyopic eye can transiently increase its contribution to binocular fusion in adults. In this study, we first asked whether dichoptic movie viewing could improve the visual function of amblyopic subjects beyond the critical period. Secondly, we tested if this effect could be enhanced by short-term monocular occlusion of the amblyopic eye. 17 subjects presenting stable functional amblyopia participated in this study. 10 subjects followed 6 sessions of 1.5 hour of dichoptic movie viewing (nonpatched group), and 7 subjects, prior to each of these sessions, had to wear an occluding patch over the amblyopic eye for two hours (patched group). Best-corrected visual acuity, monocular contrast sensitivity, interocular balance, and stereoacuity were measured before and after the training. For the nonpatched group, mean amblyopic eye visual acuity significantly improved from 0.54 to 0.46 logMAR (p < 0.05). For the patched group, mean amblyopic eye visual acuity significantly improved from 0.62 to 0.43 logMAR (p < 0.05). Stereoacuity improved significantly when the data of both groups were combined. No significant improvement was observed for the other visual functions tested. Our training procedure combines modern video technologies and recent fundamental findings in human plasticity: (i) long-term plasticity induced by dichoptic movie viewing and (ii) short-term adaptation induced by temporary monocular occlusion. This passive dichoptic movie training approach is shown to significantly improve visual acuity of subjects beyond the critical period. The addition of a short-term monocular occlusion to the dichoptic training shows promising trends but was not significant for the sample size used here. The passive movie approach combined with interocular contrast balancing even over such a short period as 2 weeks has potential as a clinical therapy to treat amblyopia in older children and adults.
Conflict of interest statement
McGill University holds two patents related to this dichoptic movie treatment. Drs. Reynaud and Hess are the named inventors. Other authors have no commercial relationships to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dichoptic training in adults with amblyopia: Additional stereoacuity gains over monocular training.Vision Res. 2018 Nov;152:84-90. doi: 10.1016/j.visres.2017.07.002. Epub 2017 Aug 4. Vision Res. 2018. PMID: 28736224
-
Binocular amblyopia treatment with contrast-rebalanced movies.J AAPOS. 2019 Jun;23(3):160.e1-160.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.jaapos.2019.02.007. Epub 2019 May 16. J AAPOS. 2019. PMID: 31103562 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental vision disorders: Do children and adolescents benefit from active vision training? IQWiG Reports – Commission No. HT21-03 [Internet].Cologne (Germany): Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG); 2023 Jul 25. Cologne (Germany): Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG); 2023 Jul 25. PMID: 37878737 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Effectiveness of a Binocular Video Game vs Placebo Video Game for Improving Visual Functions in Older Children, Teenagers, and Adults With Amblyopia: A Randomized Clinical Trial.JAMA Ophthalmol. 2018 Feb 1;136(2):172-181. doi: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2017.6090. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2018. PMID: 29302694 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The treatment of amblyopia: current practice and emerging trends.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2019 Jun;257(6):1061-1078. doi: 10.1007/s00417-019-04254-w. Epub 2019 Jan 31. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2019. PMID: 30706134 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcranial random noise stimulation and exercise do not modulate ocular dominance plasticity in adults with normal vision.J Vis. 2022 Sep 2;22(10):14. doi: 10.1167/jov.22.10.14. J Vis. 2022. PMID: 36107124 Free PMC article.
-
Action Video Gaming Does Not Influence Short-Term Ocular Dominance Plasticity in Visually Normal Adults.eNeuro. 2020 May 21;7(3):ENEURO.0006-20.2020. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0006-20.2020. Print 2020 May/Jun. eNeuro. 2020. PMID: 32345735 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging therapies for amblyopia.Semin Ophthalmol. 2021 May 19;36(4):282-288. doi: 10.1080/08820538.2021.1893765. Epub 2021 Mar 3. Semin Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 33656963 Free PMC article.
-
Binocular Approaches in Amblyopia Treatment Based on Dichoptic Stimulation.Turk J Ophthalmol. 2025 Jun 25;55(3):148-158. doi: 10.4274/tjo.galenos.2025.06626. Epub 2025 May 21. Turk J Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40395099 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rehabilitation of amblyopia using a digital platform for visual training combined with patching in children: a prospective study.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2024 Sep;262(9):3007-3020. doi: 10.1007/s00417-024-06475-0. Epub 2024 Apr 5. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 38578335 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

