Intracranial calcifications on CT: an updated review
- PMID: 31558966
- PMCID: PMC6738489
- DOI: 10.3941/jrcr.v13i8.3633
Intracranial calcifications on CT: an updated review
Abstract
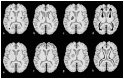
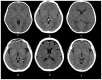
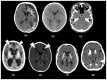
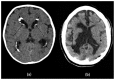
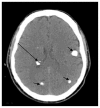
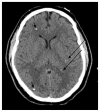
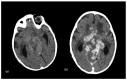
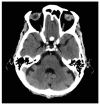
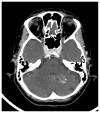
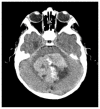
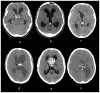
Intracranial calcifications are frequently encountered in non-contrast computed tomography scan in both adult and pediatric age groups. They refer to calcifications within the brain parenchyma or vasculature and can be classified into several major categories: physiologic/age-related, dystrophic, congenital disorders/phakomatoses, infectious, vascular, neoplastic, metabolic/endocrine, inflammatory and toxic diseases. In this updated review, we present a wide spectrum of intracranial calcifications from both pediatric and adult populations focusing on their pattern, size and location.
Keywords: Adult calcification; CT; Intracranial calcifications; Pathologic calcifications; Pediatric calcifications; Physiologic calcifications.
Figures
References
-
- Livingston JH, Stivaros S, Warren D, Crow YJ. Intracranial calcification in childhood: a review of aetiologies and recognizable phenotypes. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology. 2014 Jul;56(7):612–26. - PubMed
-
- Deng H, Zheng W, Jankovic J. Genetics and molecular biology of brain calcification. Ageing research reviews. 2015 Jul 1;22:20–38. - PubMed
-
- Yalcin A, Ceylan M, Bayraktutan OF, Sonkaya AR, Yuce I. Age and gender related prevalence of intracranial calcifications in CT imaging; data from 12,000 healthy subjects. Journal of chemical neuroanatomy. 2016 Dec 1;78:20–4. - PubMed
-
- Grech R, Grech S, Mizzi A. Intracranial Calcifications: A Pictorial Review. The neuroradiology journal. 2012 Aug;25(4):427–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical