FORWARD Study: Evaluating the Comparative Effectiveness of OnabotulinumtoxinA and Topiramate for Headache Prevention in Adults With Chronic Migraine
- PMID: 31559634
- PMCID: PMC6899480
- DOI: 10.1111/head.13653
FORWARD Study: Evaluating the Comparative Effectiveness of OnabotulinumtoxinA and Topiramate for Headache Prevention in Adults With Chronic Migraine
Abstract
Objective: To compare effectiveness of onabotulinumtoxinA and topiramate for chronic migraine (CM) prevention.
Background: The efficacy* of onabotulinumtoxinA and topiramate has been established in placebo-controlled randomized clinical trials (*defined as the benefit of treatment under ideal conditions). The effectiveness* of the 2 preventive treatments, however, has not been established (*the benefit of treatment under real-world conditions, representing a blend of efficacy and tolerability).
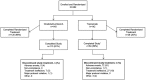
Methods: In this multicenter, randomized, parallel-group, post-authorization, open-label prospective study (FORWARD; ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT02191579), we randomized adults with CM (1:1) to onabotulinumtoxinA 155 U every 12 weeks for 3 cycles or topiramate "immediate release" 50-100 mg/day to week 36. Primary outcome measure was proportion of patients achieving ≥50% reduction in headache days (weeks 29-32). Missing values were imputed using baseline observation carried forward (BOCF) methodology. After 12 weeks, patients initially randomized to topiramate could cross over to onabotulinumtoxinA treatment. We monitored and recorded all adverse events (AEs).
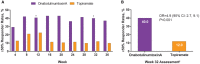
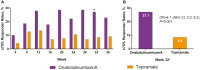
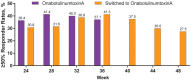
Results: We enrolled 282 patients (onabotulinumtoxinA, n = 140; topiramate, n = 142) and 148 patients completed randomized treatment (onabotulinumtoxinA, n = 120 [86%]; topiramate, n = 28 [20%]). Primary reasons for withdrawal were ineffective treatment (onabotulinumtoxinA, n = 7 [5%]; topiramate, n = 27 [19%]) and AEs (onabotulinumtoxinA, n = 5 [4%]; topiramate, n = 72 [51%]). Eighty topiramate patients crossed over to onabotulinumtoxinA. In the BOCF analysis, a significantly higher proportion of patients randomized to onabotulinumtoxinA experienced ≥50% reduction in headache frequency compared with those randomized to topiramate (40% [56/140] vs 12% [17/142], respectively; adjusted OR, 4.9 [95% CI, 2.7-9.1]; P < .001). OnabotulinumtoxinA was superior to topiramate in meeting secondary endpoints. In a post hoc analysis using observed data, the 50% responder rates at week 12 were 45.6% for onabotulinumtoxinA (n = 125) and 29.4% for topiramate (n = 109) (P = .015). AEs were reported by 48% (105/220) of onabotulinumtoxinA and 79% (112/142) of topiramate patients. Results were similar in those who crossed over to onabotulinumtoxinA.
Conclusions: While using imputation methods of accounting for differences in discontinuation rates, we found onabotulinumtoxinA to have greater clinical utility than topiramate, largely because of tolerability issues associated with the latter and a relatively higher number of onabotulinumtoxinA patients remaining on treatment.
Keywords: botulinum toxin; chronic migraine prevention; clinical utility; safety; topiramate.
© 2019 The Authors. Headache: The Journal of Head and Face Pain published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of American Headache Society.
Figures
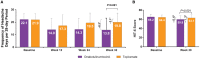
References
-
- Botox [package insert] Dublin, Ireland: Allergan Ltd. plc; 2017.
-
- Botox [summary of product characteristics] Marlow, Buckinghamshire, UK: Allergan Ltd.; 2015.
-
- Botox [product monograph] Markham, Ontario, Canada: Allergan plc; 2014.
-
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence . Botulinum toxin type A for the prevention of headaches in adults with chronic migraine. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ta260/resources/botulinum-toxin-typea-f.... Published 27 June 2012. Accessed September 20, 2019.
-
- Simpson DM, Hallett M, Ashman EJ, et al. Practice guideline update summary: Botulinum neurotoxin for the treatment of blepharospasm, cervical dystonia, adult spasticity, and headache: Report of the Guideline Development Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology. 2016;86:1818‐1826. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

