Long-term outcome of spiral ileal neobladder with orthotopic ureteral reimplantation
- PMID: 31560108
- PMCID: PMC6957550
- DOI: 10.1007/s11255-019-02296-x
Long-term outcome of spiral ileal neobladder with orthotopic ureteral reimplantation
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to analyze long-term complications, urodynamics, and quality of life (QoL) of patients after orthotopic ileal neobladder with orthotopic ureteral reimplantation to enrich clinical data and provide a basis for clinical use of this surgery.
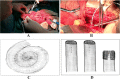
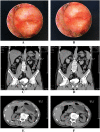
Methods: Between January 2007 and January 2013, 72 consecutive patients who underwent spiral ileal neobladder following radical cystectomy were enrolled. The neobladder was created using a modified Camey-II technique. Complications were reviewed and staged according to Clavien-Dindo classification and evaluated in long-term follow-up. Urodynamics were performed, and QoL was assessed by the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy for Bladder Cancer (FACT-BL) instrument.
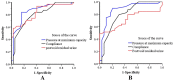
Results: The total follow-up time was 60 months, and the total survival rates at 3 and 5 years after surgery were 76.4% (55/72) and 65.3% (47/72), respectively. There were 34 (47.2%) early complications in 23 (31.9%) patients and 42 (58.3%) late complications in 35 (48.6%) patients. The total satisfactory control rates were 69.1% and 66.0% at 3 and 5 years after the surgery, respectively. Urodynamic studies were performed in some patients, and the receiver operating characteristic curve analysis showed that pressure at maximum capacity, compliance, and post void residual urine had predictive value for mortality (P < 0.05). The total FACT-BL scores of patients at 1, 3, and 5 years postoperation were 125.0 ± 15.2, 127.0 ± 16.2, and 120.6 ± 13.5, respectively, and it decreased at 5 years postoperation (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Spiral ileal neobladder with orthotopic ureteral reimplantation offers satisfactory long-term results, and urodynamic monitoring might have prognostic value.
Keywords: Ileal neobladder; Orthotopic ureteral reimplantation; Radical cystectomy; Urinary diversion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(suppl 12):277–300. - PubMed
-
- Cerruto MA, D’Elia C, Siracusano S, Porcaro AB, Cacciamani G, De Marchi D, Niero M, Lonardi C, Iafrate M, Bassi P, Belgrano E, Imbimbo C, Racioppi M, Talamini R, Ciciliato S, Toffoli L, Rizzo M, Visalli F, Verze P, Artibani W. Is health-related quality of life after radical cystectomy using validated questionnaires really better in patients with ileal orthotopic neobladder compared to ileal conduit: a meta-analysis of retrospective comparative studies. Curr Urol. 2017;10(2):57–68. doi: 10.1159/000447153. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

