Neurologic complications after allogeneic transplantation: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 31560177
- PMCID: PMC6801165
- DOI: 10.1002/acn3.50909
Neurologic complications after allogeneic transplantation: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: Neurologic adverse events remain challenging complications with poor morbidity and mortality post adult allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (allo-HCT) for hematologic diseases. We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to determine their spectrum, incidence, and impact on survival.
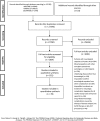
Methods: We searched MEDLINE, COCHRANE, EMBASE through March 2019 for all types of primary studies. Two independent reviewers screened, extracted data, and assessed risk of bias (RoB).
Results: We identified 552 eligible studies describing 57.972 patients; one randomized controlled trial, two case-control, 17 prospective, 86 retrospective cohort studies, 21 case series, and 425 case reports. RoB ranged from fair to high although case series were low-risk. The majority of studies traced infectious or drug-related neurologic manifestations. Infectious complications were present in 2.7% (95% CI 1.9-3.6) and 3.3% (95% CI 0.8-7.1) of patients in retrospective and prospective cohort studies, respectively. In retrospective studies, 3.4% (95% CI 2.1-4.9) of patients suffered from drug-related neurologic events. In prospective cohorts the equivalent incidence was 13% (95% CI 4.2-24.8). Neurologic complications had a detrimental impact on survival.
Interpretation: Our study highlights the wide spectrum and significant impact of neurologic complications on survival post allo-HCT. This systematic review summarizes existing data and provides the necessary background information for every physician involved in the management of these patients.
© 2019 The Authors. Annals of Clinical and Translational Neurology published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc on behalf of American Neurological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Nothing to declare.
Figures




References
-
- Tauro S, Craddock C, Peggs K, et al. Allogeneic stem‐cell transplantation using a reduced‐intensity conditioning regimen has the capacity to produce durable remissions and long‐term disease‐free survival in patients with high‐risk acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplasia. J Clin Oncol 2005;23:9387–9393. - PubMed
-
- Siegal D, Keller A, Xu W, et al. Central nervous system complications after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: incidence, manifestations, and clinical significance. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2007;13:1369–1379. - PubMed
-
- Maffini E, Festuccia M, Brunello L, et al. Neurologic Complications after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2017;23:388–397. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
