Selective Phenylimidazole-Based Inhibitors of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis Proteasome
- PMID: 31560200
- PMCID: PMC7091493
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b01187
Selective Phenylimidazole-Based Inhibitors of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis Proteasome
Abstract
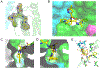
Proteasomes of pathogenic microbes have become attractive targets for anti-infectives. Coevolving with its human host, Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) has developed mechanisms to resist host-imposed nitrosative and oxidative stresses. Genetic deletion or pharmacological inhibition of the Mtb proteasome (Mtb20S) renders nonreplicating Mtb susceptible to reactive nitrogen species in vitro and unable to survive in the lungs of mice, validating the Mtb proteasome as a promising target for anti-Mtb agents. Using a structure-guided and flow chemistry-enabled study of structure-activity relationships, we developed phenylimidazole-based peptidomimetics that are highly potent for Mtb20S. X-ray structures of selected compounds with Mtb20S shed light on their selectivity for mycobacterial over human proteasomes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
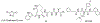

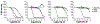
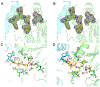
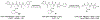
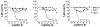

References
-
- World Health Organization, Global Tuberculosis Report 2018.
-
- Saxena AK; Singh A, Mycobacterial tuberculosis Enzyme Targets and Their Inhibitors. Curr Top Med Chem 2019, 19 (5), 337–355. - PubMed
-
- Khare S; Nagle AS; Biggart A; Lai YH; Liang F; Davis LC; Barnes SW; Mathison CJ; Myburgh E; Gao MY; Gillespie JR; Liu X; Tan JL; Stinson M; Rivera IC; Ballard J; Yeh V; Groessl T; Federe G; Koh HX; Venable JD; Bursulaya B; Shapiro M; Mishra PK; Spraggon G; Brock A; Mottram JC; Buckner FS; Rao SP; Wen BG; Walker JR; Tuntland T; Molteni V; Glynne RJ; Supek F, Proteasome Inhibition for Treatment of Leishmaniasis, Chagas Disease and Sleeping Sickness. Nature 2016, 537 (7619), 229–233. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Chemical Information

