Integrating Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics in Operational Research to End Tuberculosis
- PMID: 31560376
- PMCID: PMC7146003
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciz942
Integrating Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics in Operational Research to End Tuberculosis
Abstract
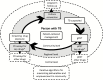
Tuberculosis (TB) elimination requires innovative approaches. The new Global Tuberculosis Network (GTN) aims to conduct research on key unmet therapeutic and diagnostic needs in the field of TB elimination using multidisciplinary, multisectorial approaches. The TB Pharmacology section within the new GTN aims to detect and study the current knowledge gaps, test potential solutions using human pharmacokinetics informed through preclinical infection systems, and return those findings to the bedside. Moreover, this approach would allow prospective identification and validation of optimal shorter therapeutic durations with new regimens. Optimized treatment using available and repurposed drugs may have an increased impact when prioritizing a person-centered approach and acknowledge the importance of age, gender, comorbidities, and both social and programmatic environments. In this viewpoint article, we present an in-depth discussion on how TB pharmacology and the related strategies will contribute to TB elimination.
Keywords: drug resistance; pharmacodynamics; pharmacokinetics; therapeutic drug monitoring; tuberculosis.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Figures
References
-
- Visca D, Zampogna E, Sotgiu G, et al. . Pulmonary rehabilitation is effective in patients with tuberculosis pulmonary sequelae. Eur Respir J 2019;53 pii: 1802184. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. WHO consolidated guidelines on drug-resistant tuberculosis treatment. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO; 2019:1–104. Available at: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/311389/9789241550529-en.... - PubMed
-
- Akkerman O, Aleksa A, Alffenaar JW, et al. ; Members of the International Study Group on New Anti-Tuberculosis Drugs and Adverse Events Monitoring Surveillance of adverse events in the treatment of drug-resistant tuberculosis: a global feasibility study. Int J Infect Dis 2019; 83:72–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

