Ketogenic Diets and Exercise Performance
- PMID: 31561520
- PMCID: PMC6835497
- DOI: 10.3390/nu11102296
Ketogenic Diets and Exercise Performance
Abstract
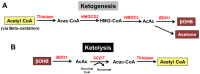
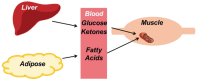
The ketogenic diet (KD) has gained a resurgence in popularity due to its purported reputation for fighting obesity. The KD has also acquired attention as an alternative and/or supplemental method for producing energy in the form of ketone bodies. Recent scientific evidence highlights the KD as a promising strategy to treat obesity, diabetes, and cardiac dysfunction. In addition, studies support ketone body supplements as a potential method to induce ketosis and supply sustainable fuel sources to promote exercise performance. Despite the acceptance in the mainstream media, the KD remains controversial in the medical and scientific communities. Research suggests that the KD or ketone body supplementation may result in unexpected side effects, including altered blood lipid profiles, abnormal glucose homeostasis, increased adiposity, fatigue, and gastrointestinal distress. The purpose of this review article is to provide an overview of ketone body metabolism and a background on the KD and ketone body supplements in the context of obesity and exercise performance. The effectiveness of these dietary or supplementation strategies as a therapy for weight loss or as an ergogenic aid will be discussed. In addition, the recent evidence that indicates ketone body metabolism is a potential target for cardiac dysfunction will be reviewed.
Keywords: endurance exercise; ketone bodies; ketone supplements; ketosis; metabolism; obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Veech R.L. The Therapeutic Implications of Ketone Bodies: The Effects of Ketone Bodies in Pathological Conditions: Ketosis, Ketogenic Diet, Redox States, Insulin Resistance, and Mitochondrial Metabolism. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids. 2004;70:309–319. doi: 10.1016/j.plefa.2003.09.007. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

