Biodistribution of Nanostructured Lipid Carriers in Mice Atherosclerotic Model
- PMID: 31561608
- PMCID: PMC6803849
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24193499
Biodistribution of Nanostructured Lipid Carriers in Mice Atherosclerotic Model
Abstract
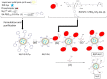
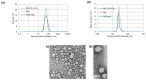
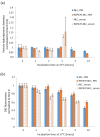
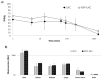
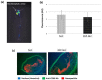
Atherosclerosis is a major cardiovascular disease worldwide, that could benefit from innovative nanomedicine imaging tools and treatments. In this perspective, we here studied, by fluorescence imaging in ApoE-/- mice, the biodistribution of non-functionalized and RXP470.1-targeted nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) loaded with DiD dye. RXP470.1 specifically binds to MMP12, a metalloprotease that is over-expressed by macrophages residing in atherosclerotic plaques. Physico-chemical characterizations showed that RXP-NLC (about 105 RXP470.1 moieties/particle) displayed similar features as non-functionalized NLC in terms of particle diameter (about 60-65 nm), surface charge (about -5 - -10 mV), and colloidal stability. In vitro inhibition assays demonstrated that RXP-NLC conserved a selectivity and affinity profile, which favored MMP-12. In vivo data indicated that NLC and RXP-NLC presented prolonged blood circulation and accumulation in atherosclerotic lesions in a few hours. Twenty-four hours after injection, particle uptake in atherosclerotic plaques of the brachiocephalic artery was similar for both nanoparticles, as assessed by ex vivo imaging. This suggests that the RXP470.1 coating did not significantly induce an active targeting of the nanoparticles within the plaques. Overall, NLCs appeared to be very promising nanovectors to efficiently and specifically deliver imaging agents or drugs in atherosclerotic lesions, opening avenues for new nanomedicine strategies for cardiovascular diseases.
Keywords: ApoE-/- model; active targeting.; atherosclerosis; lipid nanoparticles; macrophage elastase (MMP-12); nanomedicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Müller R.H., Shegokar R., Keck C.M. 20 years of lipid nanoparticles (SLN & NLC): Present state of development & industrial applications. Curr. Drug Discover. Technol. 2011;8:207–227. - PubMed
-
- Cavalli R., Marengo E., Rodriguez L., Gasco M.R. Effects of some experimental factors on the production process of solid lipid nanoparticles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 1996;42:110–115.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

