Mutant calreticulin in myeloproliferative neoplasms
- PMID: 31562135
- PMCID: PMC6923668
- DOI: 10.1182/blood.2019000622
Mutant calreticulin in myeloproliferative neoplasms
Abstract
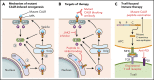
Recurrent mutations in calreticulin are present in ∼20% of patients with myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs). Since its discovery in 2013, we now have a more precise understanding of how mutant CALR, an endoplasmic reticulum chaperone protein, activates the JAK/STAT signaling pathway via a pathogenic binding interaction with the thrombopoietin receptor MPL to induce MPNs. In this Spotlight article, we review the current understanding of the biology underpinning mutant CALR-driven MPNs, discuss clinical implications, and highlight future therapeutic approaches.
© 2019 by The American Society of Hematology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: A.M. has received honoraria from Blueprint Medicines, Roche, and Incyte for invited lectures, has served on an advisory board for CTI BioPharma, and receives research support from Janssen Pharmaceuticals. G.S.H. has served on advisory boards for Agios, Celgene, Incyte, and Jazz Pharmaceuticals and has received research support from Bayer, Incyte, and Merck. J.H. declares no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Baxter EJ, Scott LM, Campbell PJ, et al. ; Cancer Genome Project . Acquired mutation of the tyrosine kinase JAK2 in human myeloproliferative disorders. Lancet. 2005;365(9464):1054-1061. - PubMed
-
- James C, Ugo V, Le Couédic JP, et al. . A unique clonal JAK2 mutation leading to constitutive signalling causes polycythaemia vera. Nature. 2005;434(7037):1144-1148. - PubMed
-
- Kralovics R, Passamonti F, Buser AS, et al. . A gain-of-function mutation of JAK2 in myeloproliferative disorders. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(17):1779-1790. - PubMed
-
- Levine RL, Wadleigh M, Cools J, et al. . Activating mutation in the tyrosine kinase JAK2 in polycythemia vera, essential thrombocythemia, and myeloid metaplasia with myelofibrosis. Cancer Cell. 2005;7(4):387-397. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

