Model organisms at the heart of regeneration
- PMID: 31562250
- PMCID: PMC6826025
- DOI: 10.1242/dmm.040691
Model organisms at the heart of regeneration
Abstract
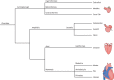
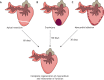
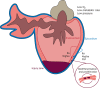
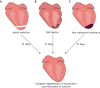
Heart failure is a major cause of death worldwide owing to the inability of the adult human heart to regenerate after a heart attack. However, many vertebrate species are capable of complete cardiac regeneration following injury. In this Review, we discuss the various model organisms of cardiac regeneration, and outline what they have taught us thus far about the cellular and molecular responses essential for optimal cardiac repair. We compare across different species, highlighting evolutionarily conserved mechanisms of regeneration and demonstrating the importance of developmental gene expression programmes, plasticity of the heart and the pathophysiological environment for the regenerative response. Additionally, we discuss how the findings from these studies have led to improvements in cardiac repair in preclinical models such as adult mice and pigs, and discuss the potential to translate these findings into therapeutic approaches for human patients following myocardial infarction.
Keywords: Cardiac regeneration; Cardiac repair; Cardiomyocytes; Myocardial infarction; Regenerative medicine.
© 2019. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Andersen D. C., Jensen C. H., Baun C., Hvidsten S., Zebrowski D. C., Engel F. B. and Sheikh S. P. (2016). Persistent scarring and dilated cardiomyopathy suggest incomplete regeneration of the apex resected neonatal mouse myocardium—A 180 days follow up study. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 90, 47-52. 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2015.11.031 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arós F., Loma-Osorio A., Vila J., López-Bescós L., Cuñat J., Rodríguez E., San José J. M., Heras M. and Marrugat J. (2006). [Effect of combined beta-blocker and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor treatment on 1-year survival after acute myocardial infarction: findings of the PRIAMHO-II registry]. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 59, 313-320. 10.1157/13087059 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

