TFF3 interacts with LINGO2 to regulate EGFR activation for protection against colitis and gastrointestinal helminths
- PMID: 31562318
- PMCID: PMC6764942
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-12315-1
TFF3 interacts with LINGO2 to regulate EGFR activation for protection against colitis and gastrointestinal helminths
Abstract
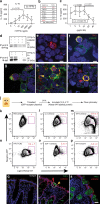
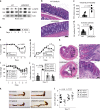
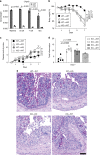
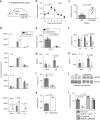
Intestinal epithelial cells (IEC) have important functions in nutrient absorption, barrier integrity, regeneration, pathogen-sensing, and mucus secretion. Goblet cells are a specialized cell type of IEC that secrete Trefoil factor 3 (TFF3) to regulate mucus viscosity and wound healing, but whether TFF3-responsiveness requires a receptor is unclear. Here, we show that leucine rich repeat receptor and nogo-interacting protein 2 (LINGO2) is essential for TFF3-mediated functions. LINGO2 immunoprecipitates with TFF3, co-localizes with TFF3 on the cell membrane of IEC, and allows TFF3 to block apoptosis. We further show that TFF3-LINGO2 interactions disrupt EGFR-LINGO2 complexes resulting in enhanced EGFR signaling. Excessive basal EGFR activation in Lingo2 deficient mice increases disease severity during colitis and augments immunity against helminth infection. Conversely, TFF3 deficiency reduces helminth immunity. Thus, TFF3-LINGO2 interactions de-repress inhibitory LINGO2-EGFR complexes, allowing TFF3 to drive wound healing and immunity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Colitis-associated variant of TLR2 causes impaired mucosal repair because of TFF3 deficiency.Gastroenterology. 2009 Jul;137(1):209-20. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2009.03.007. Epub 2009 Mar 18. Gastroenterology. 2009. PMID: 19303021 Free PMC article.
-
Delayed recanalization reduced neuronal apoptosis and neurological deficits by enhancing liver-derived trefoil factor 3-mediated neuroprotection via LINGO2/EGFR/Src signaling pathway after middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats.Exp Neurol. 2024 Jan;371:114607. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2023.114607. Epub 2023 Nov 5. Exp Neurol. 2024. PMID: 37935323 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the interplay of barrier function and leukocyte recruitment in intestinal inflammation by targeting fucosyltransferase VII and trefoil factor 3.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2010 Jul;299(1):G43-53. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00228.2009. Epub 2010 Mar 18. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20299601 Free PMC article.
-
The Intestinal Epithelium at the Forefront of Host-Helminth Interactions.Trends Parasitol. 2020 Sep;36(9):761-772. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2020.07.002. Epub 2020 Jul 23. Trends Parasitol. 2020. PMID: 32713764 Review.
-
Macrobiota - helminths as active participants and partners of the microbiota in host intestinal homeostasis.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2016 Aug;32:14-18. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2016.04.004. Epub 2016 Apr 23. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27116368 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of Serum Trefoil Factor-3 to Endoscopy in Diagnosing Helicobacter Pylori Associated Gastric Ulcer.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2020 Jul 1;21(7):2149-2153. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2020.21.7.2149. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2020. PMID: 32711444 Free PMC article.
-
Trefoil Factor Family (TFF) Peptides and Their Links to Inflammation: A Re-evaluation and New Medical Perspectives.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 6;22(9):4909. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094909. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34066339 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early Events Triggering the Initiation of a Type 2 Immune Response.Trends Immunol. 2021 Feb;42(2):151-164. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2020.11.006. Epub 2020 Dec 29. Trends Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33386241 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intestinal Trefoil Factor 3: a new biological factor mediating gut-kidney crosstalk in diabetic kidney disease.Endocrine. 2024 Apr;84(1):109-118. doi: 10.1007/s12020-023-03559-5. Epub 2023 Dec 26. Endocrine. 2024. PMID: 38148440
-
The Role of the Intestinal Epithelium in the "Weep and Sweep" Response during Gastro-Intestinal Helminth Infections.Animals (Basel). 2022 Jan 12;12(2):175. doi: 10.3390/ani12020175. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35049796 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

