Synthesis, anticancer activity, and molecular modeling of 1,4-naphthoquinones that inhibit MKK7 and Cdc25
- PMID: 31563013
- PMCID: PMC6925601
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.111719
Synthesis, anticancer activity, and molecular modeling of 1,4-naphthoquinones that inhibit MKK7 and Cdc25
Abstract
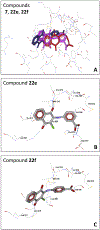
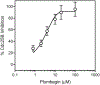
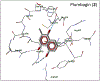
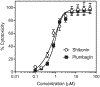
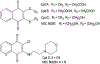
Cell division cycle 25 (Cdc25) and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 7 (MKK7) are enzymes involved in intracellular signaling but can also contribute to tumorigenesis. We synthesized and characterized the biological activity of 1,4-naphthoquinones structurally similar to reported Cdc25 and(or) MKK7 inhibitors with anticancer activity. Compound 7 (3-[(1,4-dioxonaphthalen-2-yl)sulfanyl]propanoic acid) exhibited high binding affinity for MKK7 (Kd = 230 nM), which was greater than the affinity of NSC 95397 (Kd = 1.1 μM). Although plumbagin had a lower binding affinity for MKK7, this compound and sulfur-containing derivatives 4 and 6-8 were potent inhibitors of Cdc25A and Cdc25B. Derivative 22e containing a phenylamino side chain was selective for MKK7 versus MKK4 and Cdc25 A/B, and its isomer 22f was a selective inhibitor of Cdc25 A/B. Docking studies performed on several naphthoquinones highlighted interesting aspects concerning the molecule orientation and hydrogen bonding interactions, which could help to explain the activity of the compounds toward MKK7 and Cdc25B. The most potent naphthoquinone-based inhibitors of MKK7 and/or Cdc25 A/B were also screened for their cytotoxicity against nine cancer cell lines and primary human mononuclear cells, and a correlation was found between Cdc25 A/B inhibitory activity and cytotoxicity of the compounds. Quantum chemical calculations using BP86 and ωB97X-D3 functionals were performed on 20 naphthoquinone derivatives to obtain a set of molecular electronic properties and to correlate these properties with cytotoxic activities. Systematic theoretical DFT calculations with subsequent correlation analysis indicated that energy of the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital E(LUMO), vertical electron affinity (VEA), and reactivity index ω of these molecules were important characteristics related to their cytotoxicity. The reactivity index ω was also a key characteristic related to Cdc25 A/B phosphatase inhibitory activity. Thus, 1,4-naphthoquinones displaying sulfur-containing and phenylamino side chains with additional polar groups could be successfully utilized for further development of efficacious Cdc25 A/B and MKK7 inhibitors with anticancer activity.
Keywords: Cdc25 phosphatase; Cytotoxicity; DFT analysis; Kinase inhibitor; Mitogen-activated kinase kinase 7; Molecular docking; Naphthoquinone.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
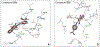
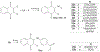
Similar articles
-
Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of novel naphthoquinone derivatives with CDC25 phosphatase inhibitory activity.Bioorg Med Chem. 2005 Aug 15;13(16):4871-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2005.05.005. Bioorg Med Chem. 2005. PMID: 15921913
-
Identification of a potent and selective pharmacophore for Cdc25 dual specificity phosphatase inhibitors.Mol Pharmacol. 2002 Apr;61(4):720-8. doi: 10.1124/mol.61.4.720. Mol Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 11901209
-
Novel naphthoquinone and quinolinedione inhibitors of CDC25 phosphatase activity with antiproliferative properties.Bioorg Med Chem. 2008 Oct 1;16(19):9040-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2008.08.009. Epub 2008 Aug 7. Bioorg Med Chem. 2008. PMID: 18789703
-
Synthetic small molecule Cdc25 phosphatases inhibitors.Curr Med Chem. 2008;15(6):573-80. doi: 10.2174/092986708783769722. Curr Med Chem. 2008. PMID: 18336271 Review.
-
CDC25A and B dual-specificity phosphatase inhibitors: potential agents for cancer therapy.Curr Med Chem. 2009;16(15):1831-49. doi: 10.2174/092986709788186084. Curr Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 19442149 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploiting the Anticancer, Antimicrobial and Antiviral Potential of Naphthoquinone Derivatives: Recent Advances and Future Prospects.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Feb 28;18(3):350. doi: 10.3390/ph18030350. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40143127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel topoisomerase II/EGFR dual inhibitors: design, synthesis and docking studies of naphtho[2',3':4,5]thiazolo[3,2-a]pyrimidine hybrids as potential anticancer agents with apoptosis inducing activity.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2023 Dec;38(1):2205043. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2023.2205043. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 37165800 Free PMC article.
-
Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of naphthalene-1,4-dione analogues as anticancer agents.RSC Med Chem. 2025 Mar 19;16(6):2677-2696. doi: 10.1039/d4md00987h. eCollection 2025 Jun 18. RSC Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 40223824 Free PMC article.
-
Non-'classical' MEKs: A review of MEK3-7 inhibitors.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2020 Jul 1;30(13):127203. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2020.127203. Epub 2020 Apr 23. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2020. PMID: 32389527 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How Substitution Combines with Non-Covalent Interactions to Modulate 1,4-Naphthoquinone and Its Derivatives Molecular Features-Multifactor Studies.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 26;22(19):10357. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910357. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34638700 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bin Hafeez B, Zhong WX, Fischer JW, Mustafa A, Shi XD, Meske L, Hong H, Cai WB, Havighurst T, Kim K, Verma AK, Plumbagin, a medicinal plant (Plumbago zeylanica)-derived 1,4-naphthoquinone, inhibits growth and metastasis of human prostate cancer PC-3M-luciferase cells in an orthotopic xenograft mouse model, Mol. Oncol 7 (2013) 428–439. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Balassiano IT, De Paulo SA, Silva NH, Cabral MC, Carvalho MDGDC, Demonstration of the lapachol as a potential drug for reducing cancer metastasis, Oncol. Rep 13 (2005) 329–333. - PubMed
-
- Carr BI, Wang Z, Kar S, K vitamins PTP antagonism, and cell growth arrest, J. Cell. Physiol 193 (2002) 263–274. - PubMed
-
- Brezak MC, Kasprzyk PG, Galcera MO, Lavergne O, Prevost GP, CDC25 inhibitors as anticancer agents are moving forward, Anti Cancer Agents Med. Chem 8 (2008) 857–862. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Chemical Information
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

