Miro1 Marks Parkinson's Disease Subset and Miro1 Reducer Rescues Neuron Loss in Parkinson's Models
- PMID: 31564441
- PMCID: PMC6893131
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2019.08.023
Miro1 Marks Parkinson's Disease Subset and Miro1 Reducer Rescues Neuron Loss in Parkinson's Models
Abstract
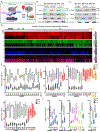
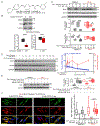
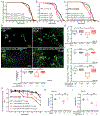
The identification of molecular targets and pharmacodynamic markers for Parkinson's disease (PD) will empower more effective clinical management and experimental therapies. Miro1 is localized on the mitochondrial surface and mediates mitochondrial motility. Miro1 is removed from depolarized mitochondria to facilitate their clearance via mitophagy. Here, we explore the clinical utility of Miro1 for detecting PD and for gauging potential treatments. We measure the Miro1 response to mitochondrial depolarization using biochemical assays in skin fibroblasts from a broad spectrum of PD patients and discover that more than 94% of the patients' fibroblast cell lines fail to remove Miro1 following depolarization. We identify a small molecule that can repair this defect of Miro1 in PD fibroblasts. Treating patient-derived neurons and fly models with this compound rescues the locomotor deficits and dopaminergic neurodegeneration. Our results indicate that tracking this Miro1 marker and engaging in Miro1-based therapies could open new avenues to personalized medicine.
Keywords: Miro1; Parkinson; biomarker; diet; fibroblast; fly; iPSC; mitochondria; mitophagy; neurons; small molecules; therapy.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
NO COMPETING FINANCIAL INTERESTS
Figures

References
-
- Bartels T (2016). Conformation-Specific Detection of alpha-Synuclein: The Search for a Biomarker in Parkinson Disease. JAMA Neurol. - PubMed
-
- Bonifati V (2002). Deciphering Parkinson’s disease--PARK8. The Lancet Neurology 1, 83. - PubMed
-
- Bruns RF, and Watson IA. (2012). Rules for identifying potentially reactive or promiscuous compounds. J Med Chem 55, 9763–9772. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

