PRDM16 Maintains Homeostasis of the Intestinal Epithelium by Controlling Region-Specific Metabolism
- PMID: 31564549
- PMCID: PMC6898778
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2019.08.017
PRDM16 Maintains Homeostasis of the Intestinal Epithelium by Controlling Region-Specific Metabolism
Abstract
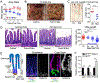
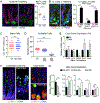
Metabolic pathways dynamically regulate tissue development and maintenance. However, the mechanisms that govern the metabolic adaptation of stem or progenitor cells to their local niche are poorly understood. Here, we define the transcription factor PRDM16 as a region-specific regulator of intestinal metabolism and epithelial renewal. PRDM16 is selectively expressed in the upper intestine, with enrichment in crypt-resident progenitor cells. Acute Prdm16 deletion in mice triggered progenitor apoptosis, leading to diminished epithelial differentiation and severe intestinal atrophy. Genomic and metabolic analyses showed that PRDM16 transcriptionally controls fatty acid oxidation (FAO) in crypts. Expression of this PRDM16-driven FAO program was highest in the upper small intestine and declined distally. Accordingly, deletion of Prdm16 or inhibition of FAO selectively impaired the development and maintenance of upper intestinal enteroids, and these effects were rescued by acetate treatment. Collectively, these data reveal that regionally specified metabolic programs regulate intestinal maintenance.
Keywords: PRDM16; apoptosis; differentiation; duodenum; fatty acid oxidation; intestinal stem cell; intestine; metabolism; transit amplifying cell.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Barker N, van Es JH, Kuipers J, Kujala P, van den Born M, Cozijnsen M, Haegebarth A, Korving J, Begthel H, Peters PJ, et al. (2007). Identification of stem cells in small intestine and colon by marker gene Lgr5. Nature 449, 1003–1007. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

