Oral absorption and lymphatic transport of baicalein following drug-phospholipid complex incorporation in self-microemulsifying drug delivery systems
- PMID: 31564878
- PMCID: PMC6735633
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S214883
Oral absorption and lymphatic transport of baicalein following drug-phospholipid complex incorporation in self-microemulsifying drug delivery systems
Abstract
Purpose: The aims of this study were to prepare a baicalein self-microemulsion with baicalein-phospholipid complex as the intermediate (BAPC-SMEDDS) and to compare its effects with those of conventional baicalein self-microemulsion (CBA-SMEDDS) on baicalein oral absorption and lymphatic transport.
Methods: Two SMEDDS were characterized by emulsifying efficiency, droplet size, zeta potential, cloud point, dilution stability, physical stability, and in vitro release and lipolysis. Different formulations of 40 mg/kg baicalein were orally administered to Sprague-Dawley rats to investigate their respective bioavailabilities. The chylomicron flow blocking rat model was used to evaluate their lymphatic transport.
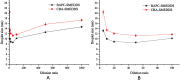
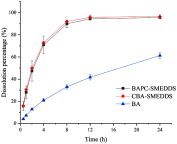
Results: The droplet sizes of BAPC-SMEDDS and CBA-SMEDDS after 100x dilution were 9.6±0.2 nm and 11.3±0.4 nm, respectively. In vivo experiments indicated that the relative bioavailability of CBA-SMEDDS and BAPC-SMEDDS was 342.5% and 448.7% compared to that of free baicalein (BA). The AUC0-t and Cmax of BAPC-SMEDDS were 1.31 and 1.87 times higher than those of CBA-SMEDDS, respectively. The lymphatic transport study revealed that 81.2% of orally absorbed BA entered the circulation directly through the portal vein, whereas approximately 18.8% was transported into the blood via lymphatic transport. CBA-SMEDDS and BAPC-SMEDDS increased the lymphatic transport ratio of BA from 18.8% to 56.2% and 70.2%, respectively. Therefore, self-microemulsion not only significantly improves oral bioavailability of baicalein, but also increases the proportion lymphatically transported. This is beneficial to the direct interaction of baicalein with relevant immune cells in the lymphatic system and for proper display of its effects.
Conclusion: This study demonstrates the oral absorption and lymphatic transport characteristics of free baicalein and baicalein SMEDDS with different compositions. This is of great significance to studies on lymphatic targeted delivery of natural immunomodulatory compounds.
Keywords: SMEDDS; baicalein; lymphatic transport; oral bioavailability; phospholipid complex.
© 2019 Liao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures









References
-
- Swartz MA. The physiology of the lymphatic system. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2001;50(1):3–20. - PubMed
-
- O’Driscoll CM. Lipid-based formulations for intestinal lymphatic delivery. Eur J Hosp Pharm. 2002;15(5):405–415. - PubMed
-
- Caliph SM, Charman WN, Porter CJH. Effect of short-, medium-, and long-chain fatty acid-based vehicles on the absolute oral bioavailability and intestinal lymphatic transport of halofantrine and assessment of mass balance in lymph-cannulated and non-cannulated rats. J Pharm Sci. 2000;89(8):1073–1084. doi:10.1002/1520-6017(200008)89:8<1073::aid-jps12>3.0.co;2-v - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pouton CW. Formulation of self-emulsifying drug delivery systems. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 1997;25(1):47–58. doi:10.1016/S0169-409X(96)00490-5 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

