Hyperspectral Raman microscopy can accurately differentiate single cells of different human thyroid nodules
- PMID: 31565498
- PMCID: PMC6757446
- DOI: 10.1364/BOE.10.004411
Hyperspectral Raman microscopy can accurately differentiate single cells of different human thyroid nodules
Abstract
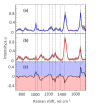
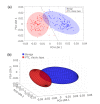
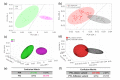
We report on the use of line-scan hyperspectral Raman microscopy in combination with multivariate statistical analyses for identifying and classifying single cells isolated from clinical samples of human thyroid nodules based on their intrinsic Raman spectral signatures. A total of 248 hyperspectral Raman images of single cells from benign thyroid (n = 127) and classic variant of papillary carcinoma (n = 121) nodules were collected. Spectral differences attributed to phenylalanine, tryptophan, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids were identified for benign and papillary carcinoma cells. Using principal component analysis and linear discriminant analysis, cells were identified with 97% diagnostic accuracy. In addition, preliminary data of cells from follicular adenoma (n = 20), follicular carcinoma (n = 25), and follicular variant of papillary carcinoma (n = 18) nodules suggest the feasibility of further discrimination of subtypes. Our findings indicate that hyperspectral Raman microscopy can potentially be developed into an objective approach for analyzing single cells from fine needle aspiration (FNA) biopsies to enable the minimally invasive diagnosis of "indeterminate" thyroid nodules and other challenging cases.
© 2019 Optical Society of America under the terms of the OSA Open Access Publishing Agreement.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Simulated fine-needle aspiration diagnosis of follicular thyroid nodules by hyperspectral Raman microscopy and chemometric analysis.J Biomed Opt. 2022 Sep;27(9):095001. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.27.9.095001. J Biomed Opt. 2022. PMID: 36071559 Free PMC article.
-
Raman-based cytopathology: an approach to improve diagnostic accuracy in medullary thyroid carcinoma.Biomed Opt Express. 2020 Nov 6;11(12):6962-6972. doi: 10.1364/BOE.410359. eCollection 2020 Dec 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2020. PMID: 33408973 Free PMC article.
-
Suggesting the cytologic diagnosis of noninvasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features (NIFTP): A retrospective analysis of atypical and suspicious nodules.Cancer Cytopathol. 2018 Feb;126(2):86-93. doi: 10.1002/cncy.21922. Epub 2017 Sep 15. Cancer Cytopathol. 2018. PMID: 28914983
-
Non-invasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features (NIFTP).J Am Soc Cytopathol. 2017 Sep-Oct;6(5):211-216. doi: 10.1016/j.jasc.2017.06.206. Epub 2017 Jul 4. J Am Soc Cytopathol. 2017. PMID: 31043245 Review.
-
The impact of non-invasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features (NIFTP) on the diagnosis of thyroid nodules.Gland Surg. 2019 Aug;8(Suppl 2):S86-S97. doi: 10.21037/gs.2018.12.01. Gland Surg. 2019. PMID: 31475095 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Simulated fine-needle aspiration diagnosis of follicular thyroid nodules by hyperspectral Raman microscopy and chemometric analysis.J Biomed Opt. 2022 Sep;27(9):095001. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.27.9.095001. J Biomed Opt. 2022. PMID: 36071559 Free PMC article.
-
Raman-based cytopathology: an approach to improve diagnostic accuracy in medullary thyroid carcinoma.Biomed Opt Express. 2020 Nov 6;11(12):6962-6972. doi: 10.1364/BOE.410359. eCollection 2020 Dec 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2020. PMID: 33408973 Free PMC article.
-
Label-Free Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy with Machine Learning for the Diagnosis of Thyroid Cancer by Using Fine-Needle Aspiration Liquid Samples.Biosensors (Basel). 2024 Jul 31;14(8):372. doi: 10.3390/bios14080372. Biosensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39194601 Free PMC article.
-
Raman Spectroscopy as a Potential Adjunct of Thyroid Nodule Evaluation: A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 13;24(20):15131. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015131. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37894812 Free PMC article.
-
Towards an Integrated Multi-Omic Approach to Improve the Diagnostic Accuracy of Fine-Needle Aspiration in Thyroid Nodules with Indeterminate Cytology.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Jun 13;15(12):1506. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15121506. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40564827 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kwong N., Medici M., Angell T. E., Liu X., Marqusee E., Cibas E. S., Krane J. F., Barletta J. A., Kim M. I., Larsen P. R., Alexander E. K., “The Influence of Patient Age on Thyroid Nodule Formation, Multinodularity, and Thyroid Cancer Risk,” J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 100(12), 4434–4440 (2015).10.1210/jc.2015-3100 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ferris R. L., Baloch Z., Bernet V., Chen A., Fahey T. J., 3rd, Ganly I., Hodak S. P., Kebebew E., Patel K. N., Shaha A., Steward D. L., Tufano R. P., Wiseman S. M., Carty S. E., “American Thyroid Association Statement on Surgical Application of Molecular Profiling for Thyroid Nodules: Current Impact on Perioperative Decision Making,” Thyroid 25(7), 760–768 (2015).10.1089/thy.2014.0502 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
