Probable Vancomycin Induced Neutropenia: A Case Report
- PMID: 31565605
- PMCID: PMC6758989
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.5199
Probable Vancomycin Induced Neutropenia: A Case Report
Abstract
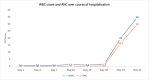
Vancomycin has been used for a long time to manage resistant gram-positive bacterial infections. Neutropenia is an uncommon and potentially serious adverse effect associated with vancomycin use. Herein we present a case of probable vancomycin induced neutropenia which resolved with discontinuation of the antibiotic. Since blood counts are monitored routinely these days in both outpatient and inpatient setting, due consideration needs to be given to vancomycin induced neutropenia in patients who are on long term antimicrobial therapy.
Keywords: neutropenia; vancomycin.
Copyright © 2019, Kaur et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Probable vancomycin-induced neutropenia.Ann Pharmacother. 2004 Nov;38(11):1855-9. doi: 10.1345/aph.1E187. Epub 2004 Oct 5. Ann Pharmacother. 2004. PMID: 15466904 Review.
-
Vancomycin-induced neutropenia resolves after substitution with teicoplanin.Clin Infect Dis. 2000 Sep;31(3):824-5. doi: 10.1086/314028. Clin Infect Dis. 2000. PMID: 11017842
-
Epidemiology of vancomycin-induced neutropenia in patients receiving home intravenous infusion therapy.Ann Pharmacother. 2006 Feb;40(2):224-8. doi: 10.1345/aph.1G436. Epub 2006 Jan 24. Ann Pharmacother. 2006. PMID: 16434560
-
Neutropenia, Thrombocytopenia, and Eosinophilia: An Unusual Triad in a Patient on Long-Term Vancomycin Therapy.Am J Case Rep. 2021 Jun 8;22:e931647. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.931647. Am J Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 34101721 Free PMC article.
-
Teicoplanin-induced hypersensitivity syndrome with a preceding vancomycin-induced neutropenia: a case report and literature review.J Clin Pharm Ther. 2010 Dec;35(6):729-32. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2710.2009.01124.x. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2010. PMID: 21054466 Review.
References
-
- Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infections: definitions and treatment. Corey GR. Clin Infect Dis. 2009;48:0. - PubMed
-
- Biopsy-proved acute tubulointerstitial nephritis and toxic epidermal necrolysis associated with vancomycin. Hsu SI. Pharmacotherapy. 2001;21:1233–1239. - PubMed
-
- The comparative efficacy and safety of teicoplanin and vancomycin. Wood MJ. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1996;37:209–222. - PubMed
-
- Vancomycin-induced toxic epidermal necrolysis. Hannah BA, Kimmel PL, Dosa S, Turner ML. South Med J. 1990;83:720–722. - PubMed
-
- Antibiotic allergy. Gruchalla RS, Pirmohamed M. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:601–609. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources