Interaction between Brucella melitensis 16M and small ubiquitin-related modifier 1 and E2 conjugating enzyme 9 in mouse RAW264.7 macrophages
- PMID: 31565897
- PMCID: PMC6769333
- DOI: 10.4142/jvs.2019.20.e54
Interaction between Brucella melitensis 16M and small ubiquitin-related modifier 1 and E2 conjugating enzyme 9 in mouse RAW264.7 macrophages
Abstract
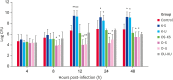
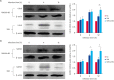
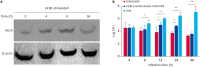
Brucella is an intracellular pathogen that invades a host and settles in its immune cells; however, the mechanism of its intracellular survival is unclear. Modification of small ubiquitin-related modifier (SUMO) occurs in many cellular activities. E2 conjugating enzyme 9 (Ubc9) is the only reported ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme that links the SUMO molecule with a target protein. Brucella's intracellular survival mechanism has not been studied with respect to SUMO-related proteins and Ubc9. Therefore, to investigate the relationship between Brucella melitensis 16M and SUMO, we constructed plasmids and cells lines suitable for overexpression and knockdown of SUMO1 and Ubc9 genes. Brucella 16M activated SUMO1/Ubc9 expression in a time-dependent manner, and Brucella 16M intracellular survival was inhibited by SUMO1/Ubc9 overexpression and promoted by SUMO1/Ubc9 depletion. In macrophages, Brucella 16M-dependent apoptosis and immune factors were induced by SUMO1/Ubc9 overexpression and restricted by SUMO1/Ubc9 depletion. We noted no effect on the expressions of SUMO1 and Ubc9 in B. melitensis 16M lipopolysaccharide-prestimulated mouse RAW264.7 macrophages. Additionally, intracellular survival of the 16M△VirB2 mutant was lower than that of Brucella 16M (p < 0.05). VirB2 can affect expression levels of Ubc9, thereby increasing intracellular survival of Brucella in macrophages at the late stage of infection. Collectively, our results demonstrate that B. melitensis 16M may use the VirB IV secretion system of Brucella to interact with SUMO-related proteins during infection of host cells, which interferes with SUMO function and promotes pathogen survival in host cells.
Keywords: Brucella; SUMO; coupling enzyme Ubc9; interaction; intracellular.
© 2019 The Korean Society of Veterinary Science.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Noncovalent interaction between Ubc9 and SUMO promotes SUMO chain formation.EMBO J. 2007 Jun 6;26(11):2797-807. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601711. Epub 2007 May 10. EMBO J. 2007. PMID: 17491593 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the interactions of HIV-1 integrase with small ubiquitin-like modifiers and their conjugation enzyme Ubc9.Int J Mol Med. 2012 Nov;30(5):1053-60. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2012.1088. Epub 2012 Aug 8. Int J Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22895527
-
Brucella Melitensis 16M Regulates the Effect of AIR Domain on Inflammatory Factors, Autophagy, and Apoptosis in Mouse Macrophage through the ROS Signaling Pathway.PLoS One. 2016 Dec 1;11(12):e0167486. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0167486. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27907115 Free PMC article.
-
SUMO Ubc9 enzyme as a viral target.IUBMB Life. 2014 Jan;66(1):27-33. doi: 10.1002/iub.1240. Epub 2014 Jan 6. IUBMB Life. 2014. PMID: 24395713 Review.
-
Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 for regulating autophagy in diabetic cardiomyopathy: A mini-review.J Diabetes. 2024 Mar;16(3):e13511. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.13511. Epub 2023 Dec 5. J Diabetes. 2024. PMID: 38052719 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Brucella infection induces chromatin restructuring in host cells to activate immune responses.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 5;16:1574006. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1574006. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40539063 Free PMC article.
-
Host SUMOylation in bacterial infections and immune defense mechanisms.Front Microbiol. 2025 Jun 26;16:1621137. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1621137. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40641872 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wareth G, Melzer F, Böttcher D, El-Diasty M, El-Beskawy M, Rasheed N, Schmoock G, Roesler U, Sprague LD, Neubauer H. Molecular typing of isolates obtained from aborted foetuses in Brucella-free Holstein dairy cattle herd after immunisation with Brucella abortus RB51 vaccine in Egypt. Acta Trop. 2016;164:267–271. - PubMed
-
- Raman N, Weir E, Müller S. The AAA ATPase MDN1 acts as a SUMO-targeted regulator in mammalian pre-ribosome remodeling. Mol Cell. 2016;64:607–615. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

