Clinical Outcomes in Early Breast Cancer With a High 21-Gene Recurrence Score of 26 to 100 Assigned to Adjuvant Chemotherapy Plus Endocrine Therapy: A Secondary Analysis of the TAILORx Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 31566680
- PMCID: PMC6777230
- DOI: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.4794
Clinical Outcomes in Early Breast Cancer With a High 21-Gene Recurrence Score of 26 to 100 Assigned to Adjuvant Chemotherapy Plus Endocrine Therapy: A Secondary Analysis of the TAILORx Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
Importance: A high 21-gene recurrence score (RS) by breast cancer assay is prognostic for distant recurrence of early breast cancer after local therapy and endocrine therapy alone, and for chemotherapy benefit.
Objective: To describe clinical outcomes for women with a high RS who received adjuvant chemotherapy plus endocrine therapy in the TAILORx trial, a population expected to have a high distant recurrence rate with endocrine therapy alone.
Design, setting, and participants: In this secondary analysis of data from a multicenter randomized clinical trial, 1389 women with hormone receptor-positive, ERBB2-negative, axillary node-negative breast cancer, and a high RS of 26 to 100 were prospectively assigned to receive adjuvant chemotherapy in addition to endocrine therapy. The analysis was conducted on May 12, 2019.
Interventions: The adjuvant chemotherapy regimen was selected by the treating physician.
Main outcomes and measures: Freedom from recurrence of breast cancer at a distant site, and freedom from recurrence, second primary cancer, and death (also known as invasive disease-free survival [IDFS]).
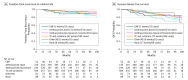
Results: Among the 9719 eligible women, with a mean age of 56 years (range 23-75 years), 1389 (14%) had a recurrence score of 26 to 100, of whom 598 (42%) had an RS of 26 to 30 and 791 (58%) had an RS of 31 to 100. The most common chemotherapy regimens included docetaxel/cyclophosphamide in 589 (42%), an anthracycline without a taxane in 334 (24%), an anthracycline and taxane in 244 (18%), cyclophosphamide/methotrexate/5-fluorouracil in 52 (4%), other regimens in 81 (6%), and no chemotherapy in 89 (6%). At 5 years, the estimated rate of freedom from recurrence of breast cancer at a distant site was 93.0% (standard error [SE], 0.8%), freedom of recurrence of breast cancer at a distant and/or local regional site 91.0% (SE, 0.8%), IDFS 87.6% (SE, 1.0%), and overall survival 95.9% (SE, 0.6%).
Conclusions and relevance: The estimated rate of freedom from recurrence of breast cancer at a distant site in women with an RS of 26 to 100 treated largely with taxane and/or anthracycline-containing adjuvant chemotherapy regimens plus endocrine therapy in the prospective TAILORx trial was 93% at 5 years, an outcome better than expected with endocrine therapy alone in this population.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT00310180.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Use of the 21-Gene Recurrence Score to Predict Clinical Outcomes in Early Breast Cancer.JAMA Oncol. 2020 Apr 1;6(4):585-586. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.6709. JAMA Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32053140 No abstract available.
-
Use of the 21-Gene Recurrence Score to Predict Clinical Outcomes in Early Breast Cancer.JAMA Oncol. 2020 Apr 1;6(4):584-585. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.6706. JAMA Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32053151 No abstract available.
-
Use of the 21-Gene Recurrence Score to Predict Clinical Outcomes in Early Breast Cancer-Reply.JAMA Oncol. 2020 Apr 1;6(4):586. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.6712. JAMA Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32053157 No abstract available.
References
-
- Albain KS, Barlow WE, Shak S, et al. ; Breast Cancer Intergroup of North America . Prognostic and predictive value of the 21-gene recurrence score assay in postmenopausal women with node-positive, oestrogen-receptor-positive breast cancer on chemotherapy: a retrospective analysis of a randomised trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11(1):55-65. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70314-6 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous