Review on Centration, Astigmatic Axis Alignment, Pupil Size and Optical Zone in SMILE
- PMID: 31567265
- PMCID: PMC6784779
- DOI: 10.1097/01.APO.0000580144.22353.46
Review on Centration, Astigmatic Axis Alignment, Pupil Size and Optical Zone in SMILE
Abstract
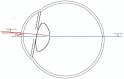
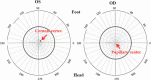
The advent of "flapless" small-incision lenticule extraction (SMILE), employing all-in-one technology, has resulted in a revolutionary breakthrough in refractive surgeries. SMILE has been gaining popularity due to fewer potential complications, such as postoperative dry eyes and greater biomechanical stability, etc. However, attention must be given to 1) the centration on the corneal vertex, 2) the proper alignment of the astigmatic axis, and 3) the relationship between pupil size and treatment diameter, to achieve good SMILE results. There is no pupil-tracking system to ascertain the accuracy of centration during the SMILE surgery. To improve the centration accuracy, our center uses two corneal topographers (Pentacam and Sirius) to measure and determine corneal vertex. Proper predicted optical zone diameter is not clearly defined yet in SMILE. Some scholars insist that mesopic pupil size should be taken into consideration when setting the predicted optical zone. Meanwhile, the issue of "functional optical zone" still has many unresolved issues and warrants further studies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Optical Zone Centration Accuracy Using Corneal Fixation-based SMILE Compared to Eye Tracker-based Femtosecond Laser-assisted LASIK for Myopia.J Refract Surg. 2015 Sep;31(9):586-92. doi: 10.3928/1081597X-20150820-03. J Refract Surg. 2015. PMID: 26352563
-
Functional Optical Zone and Centration Following SMILE and LASIK: A Prospective, Randomized, Contralateral Eye Study.J Refract Surg. 2019 Apr 1;35(4):230-237. doi: 10.3928/1081597X-20190313-01. J Refract Surg. 2019. PMID: 30984980 Clinical Trial.
-
Topographic analysis of the centration of the treatment zone after SMILE for myopia and comparison to FS-LASIK: subjective versus objective alignment.J Refract Surg. 2014 Oct;30(10):680-6. doi: 10.3928/1081597X-20140903-04. J Refract Surg. 2014. PMID: 25291751
-
Methods of Corneal Vertex Centration and Evaluation of Effective Optical Zone in Small Incision Lenticule Extraction.Ophthalmic Res. 2023;66(1):717-726. doi: 10.1159/000529922. Epub 2023 Mar 14. Ophthalmic Res. 2023. PMID: 36917962 Review.
-
Effective optical zone following small incision lenticule extraction: a review.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2024 Jun;262(6):1657-1665. doi: 10.1007/s00417-023-06263-2. Epub 2023 Oct 18. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 37851133 Review.
Cited by
-
Will SMILE Become the New Benchmark of Corneal Laser Refractive Surgery?Asia Pac J Ophthalmol (Phila). 2019 Sep-Oct;8(5):351-354. doi: 10.1097/01.APO.0000579956.14784.91. Asia Pac J Ophthalmol (Phila). 2019. PMID: 31567435 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Corneal Higher-Order Aberrations Measurements: Precision of SD-OCT/Placido Topography and Comparison with a Scheimpflug/Placido Topography in Eyes After Small-Incision Lenticule Extraction.Ophthalmol Ther. 2023 Jun;12(3):1595-1610. doi: 10.1007/s40123-023-00693-1. Epub 2023 Mar 2. Ophthalmol Ther. 2023. PMID: 36862309 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of clinical outcomes following small incision lenticule extraction performed with the visumax 800 versus visumax 500 femtosecond laser.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 15;15(1):25484. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-98041-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40664759 Free PMC article.
-
Effective optical and treatment zone analysis by means of cross-over differences after lenticule extraction.Heliyon. 2025 Jan 18;11(2):e42019. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e42019. eCollection 2025 Jan 30. Heliyon. 2025. PMID: 39911435 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of toric intraocular lens tilt and decentration measurement using dynamic Purkinje-meter and anterior segment optical coherence tomography.Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025 Mar;169(1):56-65. doi: 10.5507/bp.2024.017. Epub 2024 Jun 11. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025. PMID: 38868995 Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Zhang YJ, Shen Q, Jia Y, Zhou D, Zhou JB. Clinical outcomes of SMILE and FS-LASIK used to treat myopia: a meta-analysis. J Refract Surg 2016; 32:256–265. - PubMed
-
- Li MY, Li M, Chen YJ, et al. Five-year results of small incision lenticule extraction (SMILE) and femtosecond laser LASIK (FS-LASIK) for myopia. Acta Ophthalmol 2019; 97:E373–E380. - PubMed
-
- Lin FY, Xu YS, Yang YB. Comparison of the visual results after SMILE and femtosecond laser-assisted LASIK for myopia. J Refract Surg 2014; 30:248–254. - PubMed
-
- Ağca A, Tülü B, Yaşa D, Yildirim Y, Yildiz BK, Demirok A. Long-term (5 years) follow-up of small-incision lenticule extraction in mild-to-moderate myopia. J Cataract Refract Surg 2019; 45:421–426. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

