Short-Term Efficacy and Safety of Tolvaptan in Patients with Left Ventricular Assist Devices
- PMID: 31567410
- PMCID: PMC7340106
- DOI: 10.1097/MAT.0000000000001079
Short-Term Efficacy and Safety of Tolvaptan in Patients with Left Ventricular Assist Devices
Abstract
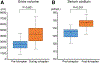
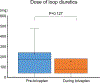
Tolvaptan is an effective therapy for heart failure patients with symptomatic congestion and hyponatremia. The efficacy of its use in patients with continuous-flow left ventricular assist devices (LVADs) is unknown. The aim of this study was to assess the clinical efficacy and safety of tolvaptan in LVAD patients. We retrospectively reviewed medical records of patients who underwent LVAD implantation between January 2014 and August 2018. Among 217 consecutive LVAD patients, tolvaptan was used in 20 patients. Mean age was 46 ± 14 years old and 14 patients were males. The duration of tolvaptan therapy was 4 (interquartile range 1-8) days. Urine volume significantly increased from 2,623 ± 1,109 ml/day before tolvaptan to 4,308 ± 1,432 ml/day during tolvaptan therapy (p < 0.001). Serum sodium increased from 127 ± 3 to 133 ± 3 mEq/L at the end of tolvaptan therapy (p < 0.001). No patients developed hypernatremia (serum sodium >150 mEq/L). The 90-day overall survival following tolvaptan therapy was 89% in both the tolvaptan group and a propensity score-matched non-tolvaptan group (p = 0.918). Survival free of heart failure readmissions was also comparable between the groups (p = 0.751). In conclusion, short-term use of tolvaptan following LVAD implantation is a safe and effective therapy to augment diuresis and improve hyponatremia.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interest: Takeo Fujino receives financial support from MSD Life Support Foundation and Mochida Memorial Foundation for Medical and Pharmaceutical Research. Nir Uriel receives grant support from Abbott and Medtronic. Gabriel Sayer is a consultant for Medtronic. Valluvan Jeevanandam is a consultant for Abbott. The other authors report no conflicts.
Figures

References
-
- Kirklin JK, Xie R, Cowger J, et al.: Second annual report from the ISHLT mechanically assisted circulatory support registry. J Heart Lung Transplant 37: 685–691, 2018. - PubMed
-
- Hasin T, Marmor Y, Kremers W, et al.: Readmissions after implantation of axial flow left ventricular assist device. J Am Coll Cardiol 61: 153–163, 2013. - PubMed
-
- Akhter SA, Badami A, Murray M, et al.: Hospital readmissions after continuous-flow left ventricular assist device implantation: Incidence, causes, and cost analysis. Ann Thorac Surg 100: 884–889, 2015. - PubMed
-
- Raina A, Seetha Rammohan HR, Gertz ZM, Rame JE, Woo YJ, Kirkpatrick JN: Postoperative right ventricular failure after left ventricular assist device placement is predicted by preoperative echocardiographic structural, hemodynamic, and functional parameters. J Card Fail 19: 16–24, 2013. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

