The menopause transition and women's health at midlife: a progress report from the Study of Women's Health Across the Nation (SWAN)
- PMID: 31568098
- PMCID: PMC6784846
- DOI: 10.1097/GME.0000000000001424
The menopause transition and women's health at midlife: a progress report from the Study of Women's Health Across the Nation (SWAN)
Abstract
Objective: Our initial understanding of the menopause transition (MT) has been framed by clinical samples of women seeking treatment rather than by population-based studies. The Study of Women's Health Across the Nation (SWAN) initiated in 1996 with an overall goal to define the MT, to characterize its biological and psychosocial antecedents and sequelae in an ethnically and racially diverse sample of midlife women.
Methods: This review summarizes the central findings of SWAN to date that can inform women and their healthcare providers about the impact of the MT and midlife aging on overall health and well-being.
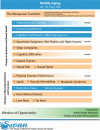
Results: SWAN characterized changes in reproductive axis and menstrual cycle patterns that informed the development of the reproductive aging staging system Staging of Reproductive Aging Workshop+10; MT-related symptoms and mental health (vasomotor symptoms, sleep complaints, psychological symptoms, cognitive performance, and urogenital and sexual health); and physiological systems and functions (cardiovascular and cardiometabolic health, bone health, physical function performance) that are influenced by the MT. SWAN demonstrated substantial interrelations among these changes and significant racial/ethnic differences in the rate and magnitude of change in multiple health indictors in midlife women. The findings point to midlife as a critical stage for adopting healthy behavior and preventive strategies.
Conclusions: Over the past 23 years, SWAN has advanced our understanding of the impact of the MT and midlife aging on health and well-being in women. SWAN will be instrumental to determine whether MT-related changes during midlife are related to unfavorable health and well-being in early old age.
Figures



References
-
- Kaufert PA. Women and their health in the middle years: a Manitoba project. Soc Sci Med 1984; 18:279–281. - PubMed
-
- McKinlay JB, McKinlay SM, Brambilla DJ. Health status and utilization behavior associated with menopause. Am J Epidemiol 1987; 125:110–121. - PubMed
-
- Matthews KA, Meilahn E, Kuller LH, Kelsey SF, Caggiula AW, Wing RR. Menopause and risk factors for coronary heart disease. N Engl J Med 1989; 321:641–646. - PubMed
-
- Guthrie JR, Dennerstein L, Taffe JR, Lehert P, Burger HG. The menopausal transition: a 9-year prospective population-based study. The Melbourne Women's Midlife Health Project. Climacteric 2004; 7:375–389. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

