Cytoneme-mediated signaling essential for tumorigenesis
- PMID: 31568500
- PMCID: PMC6786653
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008415
Cytoneme-mediated signaling essential for tumorigenesis
Abstract
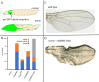
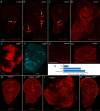
Communication between neoplastic cells and cells of their microenvironment is critical to cancer progression. To investigate the role of cytoneme-mediated signaling as a mechanism for distributing growth factor signaling proteins between tumor and tumor-associated cells, we analyzed EGFR and RET Drosophila tumor models and tested several genetic loss-of-function conditions that impair cytoneme-mediated signaling. Neuroglian, capricious, Irk2, SCAR, and diaphanous are genes that cytonemes require during normal development. Neuroglian and Capricious are cell adhesion proteins, Irk2 is a potassium channel, and SCAR and Diaphanous are actin-binding proteins, and the only process to which they are known to contribute jointly is cytoneme-mediated signaling. We observed that diminished function of any one of these genes suppressed tumor growth and increased organism survival. We also noted that EGFR-expressing tumor discs have abnormally extensive tracheation (respiratory tubes) and ectopically express Branchless (Bnl, a FGF) and FGFR. Bnl is a known inducer of tracheation that signals by a cytoneme-mediated process in other contexts, and we determined that exogenous over-expression of dominant negative FGFR suppressed tumor growth. Our results are consistent with the idea that cytonemes move signaling proteins between tumor and stromal cells and that cytoneme-mediated signaling is required for tumor growth and malignancy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Drosophila FGF cleavage is required for efficient intracellular sorting and intercellular dispersal.J Cell Biol. 2019 May 6;218(5):1653-1669. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201810138. Epub 2019 Feb 26. J Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 30808704 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk between epithelial and mesenchymal tissues in tumorigenesis and imaginal disc development.Curr Biol. 2014 Jul 7;24(13):1476-84. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2014.05.043. Curr Biol. 2014. PMID: 24980505
-
Cytoneme-mediated contact-dependent transport of the Drosophila decapentaplegic signaling protein.Science. 2014 Feb 21;343(6173):1244624. doi: 10.1126/science.1244624. Epub 2014 Jan 2. Science. 2014. PMID: 24385607 Free PMC article.
-
Cytonemes as specialized signaling filopodia.Development. 2014 Feb;141(4):729-36. doi: 10.1242/dev.086223. Development. 2014. PMID: 24496611 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulatory mechanisms of cytoneme-based morphogen transport.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022 Feb 4;79(2):119. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04148-x. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35119540 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulated delivery controls Drosophila Hedgehog, Wingless, and Decapentaplegic signaling.Elife. 2021 Jul 22;10:e71744. doi: 10.7554/eLife.71744. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34292155 Free PMC article.
-
The Drosophila epidermal growth factor receptor pathway regulates Hedgehog signalling and cytoneme behaviour.Nat Commun. 2025 Feb 26;16(1):1994. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-57162-5. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40011425 Free PMC article.
-
Hedgehog produced by the Drosophila wing imaginal disc induces distinct responses in three target tissues.Development. 2020 Nov 17;147(22):dev195974. doi: 10.1242/dev.195974. Development. 2020. PMID: 33028613 Free PMC article.
-
Airineme-Mediated Intercellular Communication.Results Probl Cell Differ. 2024;73:147-154. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-62036-2_7. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2024. PMID: 39242378 Review.
-
GPI-anchored FGF directs cytoneme-mediated bidirectional contacts to regulate its tissue-specific dispersion.Nat Commun. 2022 Jun 16;13(1):3482. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30417-1. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35710780 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

