Optimizing the sequencing of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
- PMID: 31568888
- PMCID: PMC7478849
- DOI: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2019.09.017
Optimizing the sequencing of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
Abstract
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the most common type of lung cancer, accounting for 80-85% of cases. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations are observed in approximately 40% and 20% of patients with NSCLC in Asian and non-Asian populations, respectively. First-generation (gefitinib, erlotinib) and second-generation (afatinib, dacomitinib) EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) have been standard-of-care (SoC) first-line treatment for patients with sensitizing EGFR mutation positive advanced NSCLC following Phase III trials versus platinum-based doublet chemotherapy. However, most patients treated with first-line first- or second-generation EGFR-TKIs develop resistance. Osimertinib, a third-generation, central nervous system active EGFR-TKI which potently and selectively inhibits both EGFR-TKI sensitizing (EGFRm) and the most common EGFR T790 M resistance mutations, has shown superior efficacy versus first-generation EGFR-TKIs (gefitinib / erlotinib). Osimertinib is now a treatment option for patients with advanced NSCLC harboring EGFRm in the first-line setting, and treatment of choice for patients with T790 M positive NSCLC following disease progression on first-line EGFR-TKIs. The second-generation EGFR-TKI dacomitinib has also recently been approved for the first-line treatment of EGFRm positive metastatic NSCLC. There remains a need to determine appropriate sequencing of EGFR-TKIs in this setting, including EGFR-TKIs as monotherapy or in combination with other TKIs / signaling pathway inhibitors. This review considers the evolving role of sequencing treatments to maximize benefits for patients with EGFRm positive advanced NSCLC.
Keywords: Epidermal growth factor receptor; Exon 19 deletion; Exon 21 mutation; Non-small cell lung cancer; Sequencing; Tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


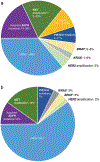
References
-
- World Health Organization. Cancer - Key facts, 2018. Available at http://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer accessed on 20 February.
-
- Planchard D, Popat S, Kerr K, Novello S, Smit EF, Faivre-Finn C, et al. Metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 2018;29:iv192–iv237. - PubMed
-
- Kalemkerian GP, Narula N, Kennedy EB, Biermann WA, Donington J, Leighl NB, et al. Molecular Testing Guideline for the Selection of Patients With Lung Cancer for Treatment With Targeted Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: American Society of Clinical Oncology Endorsement of the College of American Pathologists/International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer/Association for Molecular Pathology Clinical Practice Guideline Update. J Clin Oncol 2018;36:911–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

