Wnt Signaling in Neural Crest Ontogenesis and Oncogenesis
- PMID: 31569501
- PMCID: PMC6829301
- DOI: 10.3390/cells8101173
Wnt Signaling in Neural Crest Ontogenesis and Oncogenesis
Abstract
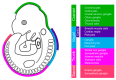
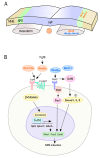
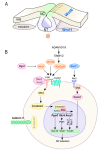
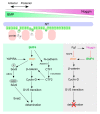
Neural crest (NC) cells are a temporary population of multipotent stem cells that generate a diverse array of cell types, including craniofacial bone and cartilage, smooth muscle cells, melanocytes, and peripheral neurons and glia during embryonic development. Defective neural crest development can cause severe and common structural birth defects, such as craniofacial anomalies and congenital heart disease. In the early vertebrate embryos, NC cells emerge from the dorsal edge of the neural tube during neurulation and then migrate extensively throughout the anterior-posterior body axis to generate numerous derivatives. Wnt signaling plays essential roles in embryonic development and cancer. This review summarizes current understanding of Wnt signaling in NC cell induction, delamination, migration, multipotency, and fate determination, as well as in NC-derived cancers.
Keywords: Wnt; neural crest stem cells; neural crest-derived cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The issue of the multipotency of the neural crest cells.Dev Biol. 2018 Dec 1;444 Suppl 1:S47-S59. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2018.03.024. Epub 2018 Mar 31. Dev Biol. 2018. PMID: 29614271 Review.
-
WNT/β-catenin signaling mediates human neural crest induction via a pre-neural border intermediate.Development. 2016 Feb 1;143(3):398-410. doi: 10.1242/dev.130849. Development. 2016. PMID: 26839343 Free PMC article.
-
WNT/β-catenin modulates the axial identity of embryonic stem cell-derived human neural crest.Development. 2019 Aug 29;146(16):dev175604. doi: 10.1242/dev.175604. Development. 2019. PMID: 31399472 Free PMC article.
-
Neural crest specification by noncanonical Wnt signaling and PAR-1.Development. 2011 Dec;138(24):5441-50. doi: 10.1242/dev.067280. Development. 2011. PMID: 22110058 Free PMC article.
-
Specification and formation of the neural crest: Perspectives on lineage segregation.Genesis. 2019 Jan;57(1):e23276. doi: 10.1002/dvg.23276. Epub 2019 Jan 15. Genesis. 2019. PMID: 30576078 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Single-cell transcriptomic analysis of zebrafish cranial neural crest reveals spatiotemporal regulation of lineage decisions during development.Cell Rep. 2021 Dec 21;37(12):110140. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.110140. Cell Rep. 2021. PMID: 34936864 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of SOX2 Repression on Corneal Endothelial Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 20;21(12):4397. doi: 10.3390/ijms21124397. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32575737 Free PMC article.
-
Prdm15 acts upstream of Wnt4 signaling in anterior neural development of Xenopus laevis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Feb 20;12:1316048. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1316048. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 38444828 Free PMC article.
-
Mouse models of patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) and their relevance for human PDA.Dev Dyn. 2022 Mar;251(3):424-443. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.408. Epub 2021 Aug 14. Dev Dyn. 2022. PMID: 34350653 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Derivation of Peripheral Nociceptive, Mechanoreceptive, and Proprioceptive Sensory Neurons from the same Culture of Human Pluripotent Stem Cells.Stem Cell Reports. 2021 Mar 9;16(3):446-457. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2021.01.001. Epub 2021 Feb 4. Stem Cell Reports. 2021. PMID: 33545066 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Trainor P.A., editor. Neural crest cells: Evolution, Development and Disease. Academic Press; London, UK: 2014. pp. 1–455.
-
- Bae C.J., Saint-Jeannet J.P. Induction and specification of neural crest cells: Extracellular signals and transcriptional switches. In: Trainor P.A., editor. Neural crest cells: Evolution, Development and Disease. Academic Press; London, UK: 2014. pp. 27–49.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

