An Efficient and Flexible Method for Deconvoluting Bulk RNA-Seq Data with Single-Cell RNA-Seq Data
- PMID: 31569701
- PMCID: PMC6830085
- DOI: 10.3390/cells8101161
An Efficient and Flexible Method for Deconvoluting Bulk RNA-Seq Data with Single-Cell RNA-Seq Data
Abstract
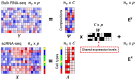
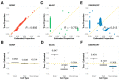
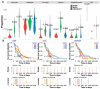
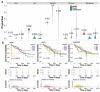
Estimating cell type compositions for complex diseases is an important step to investigate the cellular heterogeneity for understanding disease etiology and potentially facilitate early disease diagnosis and prevention. Here, we developed a computationally statistical method, referring to Multi-Omics Matrix Factorization (MOMF), to estimate the cell-type compositions of bulk RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) data by leveraging cell type-specific gene expression levels from single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) data. MOMF not only directly models the count nature of gene expression data, but also effectively accounts for the uncertainty of cell type-specific mean gene expression levels. We demonstrate the benefits of MOMF through three real data applications, i.e., Glioblastomas (GBM), colorectal cancer (CRC) and type II diabetes (T2D) studies. MOMF is able to accurately estimate disease-related cell type proportions, i.e., oligodendrocyte progenitor cells and macrophage cells, which are strongly associated with the survival of GBM and CRC, respectively.
Keywords: cell-type compositions; deconvolution; gene expression; nonnegative matrix factorization; single-cell RNA-seq.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
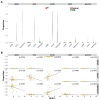
References
-
- Wagner J., Rapsomaniki M.A., Chevrier S., Anzeneder T., Langwieder C., Dykgers A., Rees M., Ramaswamy A., Muenst S., Soysal S.D., et al. A Single-Cell Atlas of the Tumor and Immune Ecosystem of Human Breast Cancer. Cell. 2019;177:1330–1345.e1318. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.03.005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Van Hove H., Martens L., Scheyltjens I., De Vlaminck K., Pombo Antunes A.R., De Prijck S., Vandamme N., De Schepper S., Van Isterdael G., Scott C.L., et al. A single-cell atlas of mouse brain macrophages reveals unique transcriptional identities shaped by ontogeny and tissue environment. Nat. Neurosci. 2019;22:1021–1035. doi: 10.1038/s41593-019-0393-4. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

