Decorin Secreted by Human Umbilical Cord Blood-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Induces Macrophage Polarization via CD44 to Repair Hyperoxic Lung Injury
- PMID: 31569732
- PMCID: PMC6801980
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20194815
Decorin Secreted by Human Umbilical Cord Blood-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Induces Macrophage Polarization via CD44 to Repair Hyperoxic Lung Injury
Abstract
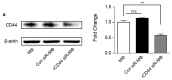
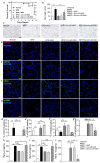
Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD), caused by hyperoxia in newborns and infants, results in lung damage and abnormal pulmonary function. However, the current treatments for BPD are steroidal and pharmacological therapies, which cause neurodevelopmental impairment. Treatment with umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells (UCB-MSCs) is an efficient alternative approach. To prevent pulmonary inflammation in BPD, this study investigated the hypothesis that a key regulator was secreted by MSCs to polarize inflammatory macrophages into anti-inflammatory macrophages at inflammation sites. Lipopolysaccharide-induced macrophages co-cultured with MSCs secreted low levels of the inflammatory cytokines, IL-8 and IL-6, but high levels of the anti-inflammatory cytokine, IL-10. Silencing decorin in MSCs suppressed the expression of CD44, which mediates anti-inflammatory activity in macrophages. The effects of MSCs were examined in a rat model of hyperoxic lung damage. Macrophage polarization differed depending on the levels of decorin secreted by MSCs. Moreover, intratracheal injection of decorin-silenced MSCs or MSCs secreting low levels of decorin confirmed impaired alveolarization of damaged lung tissues by down-regulation of decorin. In tissues, a decrease in the anti-inflammatory macrophage marker, CD163, was observed via CD44. Thus, we identified decorin as a key paracrine factor, inducing macrophage polarization via CD44, a master immunoregulator in mesenchymal stem cells.
Keywords: CD44; bronchopulmonary dysplasia; decorin; macrophage polarization; mesenchymal stem cell.
Conflict of interest statement
The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

