Impact of tumor size and nodal status on recurrence of nonfunctional pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors ≤2 cm after curative resection: A multi-institutional study of 392 cases
- PMID: 31571225
- PMCID: PMC10178766
- DOI: 10.1002/jso.25716
Impact of tumor size and nodal status on recurrence of nonfunctional pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors ≤2 cm after curative resection: A multi-institutional study of 392 cases
Abstract
Background: The current study sought to define the impact of lymph node metastasis (LNM) relative to tumor size on tumor recurrence after curative resection for nonfunctional pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (NF-pNETs) ≤2 cm.
Methods: Patients who underwent curative resection for ≤2-cm NF-pNETs were identified from a multi-institutional database. Risk factors associated with tumor recurrence as well as LNM were identified. Recurrence-free survival (RFS) was compared among patients with or without LNM.
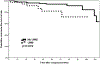
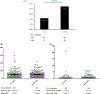
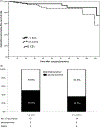
Results: A total of 392 ≤2-cm NF-pNETs patients were identified. Among the 328 patients who had lymph node dissection and evaluation, 42 (12.8%) patients had LNM. LNM was associated with tumor recurrence (hazard ratio, 3.06; P = .026) after surgery. RFS was worse among LNM vs no LNM patients (5-year RFS, 81.7% vs 94.1%; P = .019). Patients with tumors measuring 1.5-2 cm had a two-fold increase in the incidence of LNM vs patients with tumors <1.5 cm (17.9% vs 8.7%, odds ratio, 2.59; P = .022), as well as a higher risk of advanced tumor grade and higher Ki-67 levels (both P < .01). After curative resection, a total of 14 (8.0%) patients with a tumor of 1.5-2 cm and 10 (4.5%) patients with tumor <1.5 cm developed tumor recurrence.
Conclusion: Surgical resection with lymphadenectomy should be considered for patients with NF-pNETs ≥1.5-2.0 cm.
Keywords: lymph node metastasis; neuroendocrine tumor; pancreas; surgery; tumor size.
© 2019 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTERESTS
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Bilimoria KY, Talamonti MS, Tomlinson JS, et al. Prognostic score predicting survival after resection of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: analysis of 3851 patients. Ann Surg. 2008;247:490–500. - PubMed
-
- Yang G, Ji M, Chen J, et al. Surgery management for sporadic small (≤2 cm), non-functioning pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: A consensus statement by the Chinese Study Group for Neuroendocrine Tumors (CSNET). Int J Oncol. 2017;50:567–574. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

