Differences in oxytocin and vasopressin levels in individuals suffering from the autism spectrum disorders vs general population - a systematic review
- PMID: 31571878
- PMCID: PMC6750159
- DOI: 10.2147/NDT.S207580
Differences in oxytocin and vasopressin levels in individuals suffering from the autism spectrum disorders vs general population - a systematic review
Abstract
Introduction: Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by deficits in social interactions, communication, and the presence of stereotyped, repetitive behaviors. Oxytocin (OXT) and arginine-vasopressin are neuropeptides produced in hypothalamus and they are related to processing emotions and social behavior. In the light of a growing number of scientific reports related to this issue, the two neurohormones started to be linked with the basis of neurodevelopmental disorders, including the ASD. The aim of this study was a systematic review of previous studies regarding the differences in OXT and vasopressin levels in ASD and neurotypical persons.
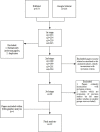
Materials and methods: Literature review focused on publications in the last 10 years located via the MEDLINE/PubMed database as well as the Google Scholar browser. Selection was made by assumptive criteria of inclusion and exclusion.
Results: From the 487 studies qualified to the initial abstract analysis, 12 met the six inclusion criteria and were included in the full-text review.
Conclusion: Currently, available study reports still do not provide unequivocal answers as to the differences in concentrations of those neuropeptides between children with ASD and neurotypical control. Therefore, it is necessary to continue the research taking into account necessity of proper homogenization of study groups, utilization of objective and quantifiable tools for ASD diagnosis and broadening the range of biochemical and molecular factors analyzed.
Keywords: ASD; AVP; OXT; autism spectrum disorder; oxytocin; vasopressin.
© 2019 Wilczyński et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association: Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association;2013.
-
- Yates K, Le CA, Szczęsny E (tłumaczenie)Diagnostyka autyzmu. Paediatr Child Heal.2009;19:55–59. doi:10.1016/j.paed.2008.10.010 - DOI
-
- Rybakowski F, Białek A, Chojnicka I, et al. Zaburzenia ze spektrum autyzmu - epidemiologia, objawy, współzachorowalnos̈ć i rozpoznawanie. Psychiatr Pol. 2014;48(4):653–665. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous