A novel CXCL8 analog is effective in inhibiting the growth via cell cycle arrest and attenuating invasion of Lewis lung carcinoma
- PMID: 31571912
- PMCID: PMC6754332
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S215824
A novel CXCL8 analog is effective in inhibiting the growth via cell cycle arrest and attenuating invasion of Lewis lung carcinoma
Abstract
Purpose: Lung cancer and other solid tumors contain not only tumor cells but various types of stromal cells, such as fibroblasts and endothelial cells. In addition, tumors are infiltrated by inflammatory cells (neutrophils, macrophages, and lymphocytes). Tumor cells, stromal cells, and the tumor-associated leukocytes are responsible for the production of chemokines inside the tumor and the maintenance of systemic circulating chemokine levels. CXCL8 and its receptors, CXCR1 and CXCR2, were found to play important roles in tumor proliferation, migration, survival, and growth. We have developed a novel ELR-CXC chemokine antagonist CXCL8-IP10 based on the structure of CXCL8 and IP10.
Patients and methods: We assessed the anticancer efficacies of the blockade of CXCL8-CXCR1/2 axis in the Lewis lung carcinoma (LL/2) model using CXCL8-IP10.
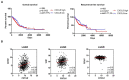
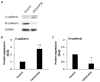
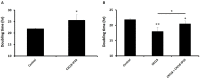
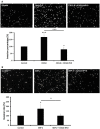
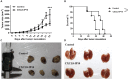
Results: We found that CXCL8-IP10 markedly reduced LL/2 cell anchorage-independent growth and invasion. Moreover, we demonstrated that CXCL8-IP10 could significantly suppress tumor growth and improve survival rate as well as lifespan of C57BL/6 mice inoculated with LL/2 cells.
Conclusion: Our results suggest that ELR-CXC chemokine antagonism would potentially be a useful therapeutic approach in patients with lung cancer.
Keywords: CXCL8; CXCR1; CXCR2; Lewis lung carcinoma; antagonist.
© 2019 Hsu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
We report the industrial-academic collaboration grant from Rise Biopharmaceuticals Inc. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
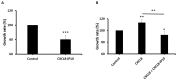
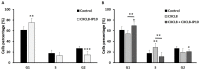
Similar articles
-
CXCR1/2 antagonism with CXCL8/Interleukin-8 analogue CXCL8(3-72)K11R/G31P restricts lung cancer growth by inhibiting tumor cell proliferation and suppressing angiogenesis.Oncotarget. 2015 Aug 28;6(25):21315-27. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4066. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26087179 Free PMC article.
-
Fine-Tuning of GPCR-Chemokine Interactions. Design and Identification of Chemokine Analogues as Receptor Agonists, Biased Agonists, and Antagonists.Biochemistry. 2019 Mar 12;58(10):1432-1439. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.8b01266. Epub 2019 Feb 21. Biochemistry. 2019. PMID: 30726064
-
A novel CXCL8-IP10 hybrid protein is effective in blocking pulmonary pathology in a mouse model of Klebsiella pneumoniae infection.Int Immunopharmacol. 2018 Sep;62:40-45. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2018.06.040. Epub 2018 Jul 3. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29990693
-
Combined anti CXC receptors 1 and 2 therapy is a promising anti-inflammatory treatment for respiratory diseases by reducing neutrophil migration and activation.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2015 Oct;34:37-45. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2015.08.002. Epub 2015 Aug 10. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2015. PMID: 26271598 Review.
-
An updated review on the role of the CXCL8-CXCR1/2 axis in the progression and metastasis of breast cancer.Mol Biol Rep. 2021 Sep;48(9):6551-6561. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06648-8. Epub 2021 Aug 24. Mol Biol Rep. 2021. PMID: 34426905 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of Cost and Potency of Human Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Conditioned Medium Derived from 2- and 3-Dimensional Cultures.Bioengineering (Basel). 2023 Aug 4;10(8):930. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering10080930. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37627815 Free PMC article.
-
Implications of ZNF334 gene in lymph node metastasis of lung SCC: potential bypassing of cellular senescence.J Transl Med. 2024 Apr 18;22(1):372. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05115-9. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38637790 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

