Inhibition of esophageal cancer growth through the suppression of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- PMID: 31571914
- PMCID: PMC6756275
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S205457
Inhibition of esophageal cancer growth through the suppression of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
Abstract
Background: The phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT)/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway is implicated in several cancers. AKT allosteric inhibitor MK2206 and dual PI3K and mTOR inhibitor BEZ235 are promising drug candidates with potential anti-tumor effects.
Purpose: In this study, we aimed to detect the activation of PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and assess the efficacy of MK2206 and BEZ235 in inhibiting esophageal cancer growth.
Materials and methods: We used three different systems including carcinogen-induced animal model, human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) cell lines, and xenograft mouse model.
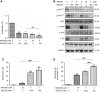
Results: Our data indicated that components of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway were overexpressed and activated in esophageal SCC. MK2206 and BEZ235 inhibited cell proliferation, enhanced apoptosis, and induced cell-cycle arrest through downstream effectors SKP2, MCL-1, and cyclin D1 in esophageal SCC cells. MK2206 and BEZ235 also inhibited tumor growth in xenograft mice through the inhibition of AKT phosphorylation. MK2206/BEZ235 combination showed greater anti-tumor effect than MK2206 or BEZ235 alone. The enhanced efficacy of the combination was associated with the inhibition of phosphorylation ATK on both Thr308 and Ser473.
Conclusion: The combination of MK2206 and BEZ235 exhibits potent antitumor effects and may have important clinical applications for esophageal SCC treatment.
Keywords: BEZ235; Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; MK2206; PI3K/AKT/mTOR.
© 2019 Shi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures





References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

