Effect of glutaminase inhibition on cancer-induced bone pain
- PMID: 31571981
- PMCID: PMC6750878
- DOI: 10.2147/BCTT.S215655
Effect of glutaminase inhibition on cancer-induced bone pain
Abstract
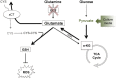
Purpose: The complex nature of cancer-induced bone pain (CIBP) has led to investigation into cancer-targeted therapies. This has involved targeting glutamate release from the tumor, secreted as a byproduct of antioxidant responses and metabolic disruption. Cancer cells undergo many metabolic changes that result in increased glutamine metabolism and subsequently the production of glutamate. Glutaminase (GLS) is the enzyme that mediates the conversion of glutamine to glutamate and has been shown to be upregulated in many cancer types including malignancies of the breast. This enzyme, therefore, represents another potential therapeutic target for CIBP, one that lies upstream of glutamate secretion.
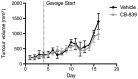
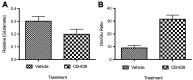
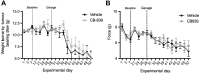
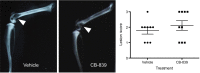
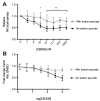
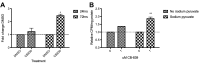
Methods: A recently developed inhibitor of GLS, CB-839, was tested in an animal model of CIBP induced by intrafemoral MDA-MB-231 xenografts. CIBP behaviors were assessed using Dynamic Weight Bearing and Dynamic Plantar Aesthesiometer readings of mechanical hyperalgesia and allodynia.
Results: CB-839 failed to modulate any of the associated nociceptive behaviors induced by intrafemoral MDA-MB-231 tumor growth. Further investigation in vitro revealed the sensitivity of the drug is dependent on the metabolic flexibility of the cell line being tested which can be modulated by cell culture environment.
Conclusion: Adaptation to metabolic disturbances may explain the failure of CB-839 to exhibit any significant effects in vivo and the metabolic flexibility of the cell line tested should be considered for future investigations studying the metabolic effects of glutaminase inhibition.
Keywords: Cancer-induced bone pain; anaplerosis; breast cancer; glutaminase.
© 2019 Fazzari and Singh.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Glutamine to proline conversion is associated with response to glutaminase inhibition in breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res. 2019 May 14;21(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s13058-019-1141-0. Breast Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31088535 Free PMC article.
-
Pyruvate anaplerosis is a mechanism of resistance to pharmacological glutaminase inhibition in triple-receptor negative breast cancer.BMC Cancer. 2020 May 25;20(1):470. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-06885-3. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32450839 Free PMC article.
-
Glutaminase inhibitor CB-839 increases radiation sensitivity of lung tumor cells and human lung tumor xenografts in mice.Int J Radiat Biol. 2019 Apr;95(4):436-442. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2018.1558299. Epub 2019 Jan 15. Int J Radiat Biol. 2019. PMID: 30557074 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Development of Small Molecule Glutaminase Inhibitors.Curr Top Med Chem. 2018;18(6):432-443. doi: 10.2174/1568026618666180525100830. Curr Top Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29793408 Review.
-
The role of glutaminase in cancer.Histopathology. 2020 Mar;76(4):498-508. doi: 10.1111/his.14014. Epub 2020 Feb 18. Histopathology. 2020. PMID: 31596504 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of eEF2K synergizes with glutaminase inhibitors or 4EBP1 depletion to suppress growth of triple-negative breast cancer cells.Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 28;11(1):9181. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-88816-1. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33911160 Free PMC article.
-
The unique catalytic properties of PSAT1 mediate metabolic adaptation to glutamine blockade.Nat Metab. 2024 Aug;6(8):1529-1548. doi: 10.1038/s42255-024-01104-w. Epub 2024 Aug 27. Nat Metab. 2024. PMID: 39192144
-
Potential therapeutic treatments of cancer-induced bone pain.Curr Opin Support Palliat Care. 2020 Jun;14(2):107-111. doi: 10.1097/SPC.0000000000000496. Curr Opin Support Palliat Care. 2020. PMID: 32349095 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Analgesics with Peripheral Targets.Neurotherapeutics. 2020 Jul;17(3):784-825. doi: 10.1007/s13311-020-00937-z. Epub 2020 Oct 15. Neurotherapeutics. 2020. PMID: 33063247 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

