Role of Neurofilament Light Chain as a Potential Biomarker for Alzheimer's Disease: A Correlative Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 31572170
- PMCID: PMC6753203
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2019.00254
Role of Neurofilament Light Chain as a Potential Biomarker for Alzheimer's Disease: A Correlative Meta-Analysis
Abstract
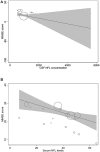
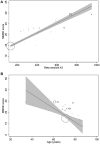
Neurofilament light (NFL) is a putative biomarker of neurodegeneration. This study evaluates the correlative association of NFL with Alzheimer's disease (AD) indices. Relevant studies were identified after a literature search in electronic databases and study selection was based on pre-determined eligibility criteria. Correlation coefficients between NFL levels and important AD indices reported by individual studies were pooled as z-scores. Meta-regression analyses were performed to evaluate the relationships between important covariates. Data from 38 studies (age 68.3 years [95% confidence interval (CI): 65.7, 70.9]; 54 % [95% CI: 50, 57] females) were used. Meta-analyses of correlation coefficients reported by the included studies showed that NFL levels in blood and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) correlated well (r = 0.59 [95% CI: 0.45, 0.71]; p < 0.0001). NFL levels correlated with MMSE score (r = -0.345 [95% CI: -0.43, -0.25]; p = 0.0001), and age (r = 0.485 [95% CI: 0.35, 0.61]; p = 0.00001). CSF NFL levels correlated with total tau (t-tau; r = 0.39 [95% CI: 0.27, 0.50]; p = 0.0001), phosphorylated tau (p-tau; r = 0.34 [95% CI: 0.19, 0.47]; p = 0.00001), and neurogranin (r = 0.25 [95% CI: 0.12, 0.37]; p = 0.001) but not with beta amyloid (Aβ) (r = 0.00 [95%CI: -0.13, 0.12]; p = 0.937). In meta-regression, MMSE scores were associated inversely with blood NFL (metaregression coefficient (MC) -0.236 [95% CI:-0.40, -0.072; p = 0.008), and age (MC) -0.235 [-0.36, -0.11]; p = 0.001) and positively with CSF Aβ-42 (MC 0.017 [0.010, 0.023]; p = 0.00001). NFL has good correlations with t-tau, and p-tau in CSF and CSF NFL levels correlates well with blood NFL levels. These results show that NFL can be a useful biomarker for improving diagnosis and predicting prognosis in AD patients especially if age weighted.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; biomarker; correlation; diagnosis; neurofilament light.
Copyright © 2019 Jin, Cao and Dai.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Cerebrospinal fluid tau, neurogranin, and neurofilament light in Alzheimer's disease.EMBO Mol Med. 2016 Oct 4;8(10):1184-1196. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201606540. Print 2016 Oct. EMBO Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 27534871 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma tau, neurofilament light chain and amyloid-β levels and risk of dementia; a population-based cohort study.Brain. 2020 Apr 1;143(4):1220-1232. doi: 10.1093/brain/awaa054. Brain. 2020. PMID: 32206776 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between Longitudinal Plasma Neurofilament Light and Neurodegeneration in Patients With Alzheimer Disease.JAMA Neurol. 2019 Jul 1;76(7):791-799. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.0765. JAMA Neurol. 2019. PMID: 31009028 Free PMC article.
-
Neurofilament Light Chain as a Potential Biomarker in Plasma for Alzheimer's Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Systematic Review and a Meta-Analysis.J Integr Neurosci. 2023 Jun 30;22(4):85. doi: 10.31083/j.jin2204085. J Integr Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37519166
-
Fluid biomarker-based molecular phenotyping of Alzheimer's disease patients in research and clinical settings.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2019;168:3-23. doi: 10.1016/bs.pmbts.2019.07.006. Epub 2019 Jul 24. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2019. PMID: 31699324 Review.
Cited by
-
Neurofilament light chain in the vitreous humor of the eye.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2020 Sep 17;12(1):111. doi: 10.1186/s13195-020-00677-4. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 32943089 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between blood selenium and serum neurofilament light chain: results of a nationwide survey.Front Neurol. 2025 Apr 8;16:1490760. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1490760. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40264648 Free PMC article.
-
Blood-Based β-Amyloid and Phosphorylated Tau (p-Tau) Biomarkers in Alzheimer's Disease: A Systematic Review of Their Diagnostic Potential.Cureus. 2025 Mar 1;17(3):e79881. doi: 10.7759/cureus.79881. eCollection 2025 Mar. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40166792 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasma N-terminal tau fragment levels predict future cognitive decline and neurodegeneration in healthy elderly individuals.Nat Commun. 2020 Nov 27;11(1):6024. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19543-w. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 33247134 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma neurofilament light and brain volumetric outcomes among middle-aged urban adults.Neurobiol Aging. 2023 Sep;129:28-40. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2023.04.013. Epub 2023 May 2. Neurobiol Aging. 2023. PMID: 37257406 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ashton N., Leuzy A., Lim Y. M., Troakes C., Hortobágyi T., Hoglund K., et al. . (2019). Increased plasma neurofilament light chain concentration correlates with severity of post-mortem neurofibrillary tangle pathology and neurodegeneration. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 7:5. 10.1186/s40478-018-0649-3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bettcher B. M., Johnson S. C., Fitch R., Casaletto K. B., Heffernan K. S., Asthana S., et al. . (2018). Cerebrospinal fluid and plasma levels of inflammation differentially relate to CNS markers of Alzheimer's disease pathology and neuronal damage. J. Alzheimers Dis. 62, 385–397. 10.3233/JAD-170602 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

