Assessing Visual Statistical Learning in Early-School-Aged Children: The Usefulness of an Online Reaction Time Measure
- PMID: 31572261
- PMCID: PMC6753232
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.02051
Assessing Visual Statistical Learning in Early-School-Aged Children: The Usefulness of an Online Reaction Time Measure
Abstract
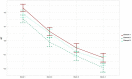
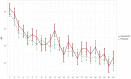
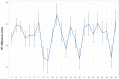
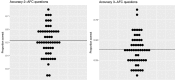
Visual statistical learning (VSL) was traditionally tested through offline two-alternative forced choice (2-AFC) questions. More recently, online reaction time (RT) measures and alternative offline question types have been developed to further investigate learning during exposure and more adequately assess individual differences in adults (Siegelman et al., 2017b, 2018). We assessed the usefulness of these measures for investigating VSL in early-school-aged children. Secondarily, we examined the effect of introducing a cover task, potentially affecting attention, on children's VSL performance. Fifty-three children (aged 5-8 years) performed a self-paced VSL task containing triplets, in which participants determine the presentation speed and RTs to each stimulus are recorded. Half of the participants performed a cover task, while the other half did not. Online sensitivity to the statistical structure was measured by contrasting RTs to unpredictable versus predictable elements. Subsequently, participants completed 2-AFC (choose correct triplet) and 3-AFC (fill blank to complete triplet) offline questions. RTs were significantly longer for unpredictable than predictable elements, so we conclude that early-school-aged children are sensitive to the statistical structure during exposure, and that the RT task can measure that. We found no evidence as to whether children can perform above chance on offline 2-AFC or 3-AFC questions, or whether the cover task affects children's VSL performance. These results show the feasibility of using an online RT task when assessing VSL in early-school-aged children. This task therefore seems suitable for future studies that aim to investigate VSL across development or in clinical populations, perhaps together with behavioral tasks.
Keywords: children; online measure; reaction time; statistical learning; visual.
Copyright © 2019 van Witteloostuijn, Lammertink, Boersma, Wijnen and Rispens.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Opposing Timing Constraints Severely Limit the Use of Pupillometry to Investigate Visual Statistical Learning.Front Psychol. 2019 Aug 6;10:1792. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.01792. eCollection 2019. Front Psychol. 2019. PMID: 31447735 Free PMC article.
-
Visual statistical learning in children and young adults: how implicit?Front Psychol. 2015 Jan 8;5:1541. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2014.01541. eCollection 2014. Front Psychol. 2015. PMID: 25620943 Free PMC article.
-
Online measurement of learning temporal statistical structure in categorization tasks.Mem Cognit. 2022 Oct;50(7):1530-1545. doi: 10.3758/s13421-022-01302-5. Epub 2022 Apr 4. Mem Cognit. 2022. PMID: 35377057 Free PMC article.
-
[Aiming for zero blindness].Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2015 Mar;119(3):168-93; discussion 194. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2015. PMID: 25854109 Review. Japanese.
-
The developmental origins of naïve psychology in infancy.Adv Child Dev Behav. 2009;37:55-104. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2407(09)03702-1. Adv Child Dev Behav. 2009. PMID: 19673160 Review.
Cited by
-
Speech Stream Composition Affects Statistical Learning: Behavioral and Neural Evidence.Brain Sci. 2025 Feb 14;15(2):198. doi: 10.3390/brainsci15020198. Brain Sci. 2025. PMID: 40002530 Free PMC article.
-
Learning Words While Listening to Syllables: Electrophysiological Correlates of Statistical Learning in Children and Adults.Front Hum Neurosci. 2022 Feb 23;16:805723. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2022.805723. eCollection 2022. Front Hum Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35280206 Free PMC article.
-
Statistical learning abilities of children with dyslexia across three experimental paradigms.PLoS One. 2019 Aug 5;14(8):e0220041. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0220041. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31381565 Free PMC article.
-
Explicit Instructions Do Not Enhance Auditory Statistical Learning in Children With Developmental Language Disorder: Evidence From Event-Related Potentials.Front Psychol. 2022 Jun 30;13:905762. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.905762. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 35846717 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

