Persistence of a T Cell Infiltrate in Human Ganglia Years After Herpes Zoster and During Post-herpetic Neuralgia
- PMID: 31572325
- PMCID: PMC6749866
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02117
Persistence of a T Cell Infiltrate in Human Ganglia Years After Herpes Zoster and During Post-herpetic Neuralgia
Abstract
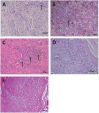
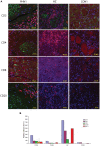
Varicella-zoster virus (VZV) is a human herpesvirus which causes varicella (chicken pox) during primary infection, establishes latency in sensory ganglia, and can reactivate from this site to cause herpes zoster (HZ) (shingles). A major complication of HZ is a severe and often debilitating pain called post-herpetic neuralgia (PHN) which persists long after the resolution of the HZ-associated rash. The underlying cause of PHN is not known, although it has been postulated that it may be a consequence of immune cell mediated damage. However, the nature of virus-immune cell interactions within ganglia during PHN is unknown. We obtained rare formalin fixed paraffin embedded sections cut from surgically excised ganglia from a PHN-affected patient years following HZ rash resolution. VZV DNA was readily detected by qPCR and regions of immune infiltration were detected by hematoxylin and eosin staining. Immunostaining using a range of antibodies against immune cell subsets revealed an immune cell response comprising of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells and CD20+ B cells. This study explores the immune cell repertoire present in ganglia during PHN and provides evidence for an ongoing immune cell inflammation years after HZ.
Keywords: ganglia; herpes zoster (HZ); immune cell; post-herpetic neuralgia (PHN); varicella-zoster virus.
Copyright © 2019 Sutherland, Steain, Buckland, Rodriguez, Cunningham, Slobedman and Abendroth.
Figures

References
-
- Bennett G. J. (1994). Hypotheses on the pathogenesis of herpes zoster-associated pain. Ann. Neurol. 35(Supp l), S38–S41. - PubMed
-
- Cohrs R. J., Randall J., Smith J., Gilden D. H., Dabrowski C., van Der Keyl H., et al. (2000). Analysis of individual human trigeminal ganglia for latent herpes simplex virus type 1 and varicella-zoster virus nucleic acids using real-time PCR. J. Virol. 74 11464–11471. 10.1128/jvi.74.24.11464-11471.2000 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Coplan P. M., Schmader K., Nikas A., Chan I. S., Choo P., Levin M. J., et al. (2004). Development of a measure of the burden of pain due to herpes zoster and postherpetic neuralgia for prevention trials: adaptation of the brief pain inventory. J. Pain 5 344–356. 10.1016/j.jpain.2004.06.001 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

