Quorum Sensing Signaling Alters Virulence Potential and Population Dynamics in Complex Microbiome-Host Interactomes
- PMID: 31572336
- PMCID: PMC6749037
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02131
Quorum Sensing Signaling Alters Virulence Potential and Population Dynamics in Complex Microbiome-Host Interactomes
Abstract
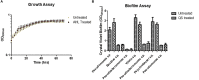
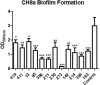
Despite the discovery of the first N-acyl homoserine lactone (AHL) based quorum sensing (QS) in the marine environment, relatively little is known about the abundance, nature and diversity of AHL QS systems in this diverse ecosystem. Establishing the prevalence and diversity of AHL QS systems and how they may influence population dynamics within the marine ecosystem, may give a greater insight into the evolution of AHLs as signaling molecules in this important and largely unexplored niche. Microbiome profiling of Stelletta normani and BD1268 sponge samples identified several potential QS active genera. Subsequent biosensor-based screening of a library of 650 marine sponge bacterial isolates identified 10 isolates that could activate at least one of three AHL biosensor strains. Each was further validated and profiled by Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry, with AHLs being detected in 8 out of 10 isolate extracts. Co-culture of QS active isolates with S. normani marine sponge samples led to the isolation of genera such as Pseudomonas and Paenibacillus, both of which were low abundance in the S. normani microbiome. Surprisingly however, addition of AHLs to isolates harvested following co-culture did not measurably affect either growth or biofilm of these strains. Addition of supernatants from QS active strains did however impact significantly on biofilm formation of the marine Bacillus sp. CH8a sporeforming strain suggesting a role for QS systems in moderating the microbe-microbe interaction in marine sponges. Genome sequencing and phylogenetic analysis of a QS positive Psychrobacter isolate identified several QS associated systems, although no classical QS synthase gene was identified. The stark contrast between the biodiverse sponge microbiome and the relatively limited diversity that was observed on standard culture media, even in the presence of QS active compounds, serves to underscore the extent of diversity that remains to be brought into culture.
Keywords: acyl homoserine lactone (AHL); cell–cell communication; marine sponge-associated bacteria; microbiome; quorum sensing (QS).
Copyright © 2019 Reen, Gutiérrez-Barranquero, McCarthy, Woods, Scarciglia, Adams, Fog Nielsen, Gram and O’Gara.
Figures




References
-
- Abbamondi G. R., De Rosa S., Iodice C., Tommonaro G. (2014). Cyclic dipeptides produced by marine sponge-associated bacteria as quorum sensing signals. Nat. Prod. Comm. 9 229–232. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

