Development and Clinical Validation of Multiple Cross Displacement Amplification Combined With Nanoparticles-Based Biosensor for Detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis: Preliminary Results
- PMID: 31572340
- PMCID: PMC6753184
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02135
Development and Clinical Validation of Multiple Cross Displacement Amplification Combined With Nanoparticles-Based Biosensor for Detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis: Preliminary Results
Abstract
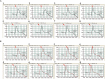
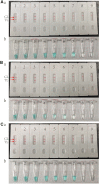
Tuberculosis is still a major threat to global public health. Here, a novel diagnosis assay, termed as multiple cross displacement amplification combined with nanoparticle-based lateral flow biosensor (MCDA-LFB), was developed to simultaneously detect IS6110 and IS1081 of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) in DNA extracted from reference strain H37Rv and clinical samples. The amplification can be finished within 30 min at a fixed temperature (67°C), thus the whole procedure, including rapid template preparation (15 min), isothermal reaction (30 min) and result reporting (2 min), can be completed within 50 min. The limit of detection of multiplex MCDA assay was 10 fg per reaction. By using the multiplex MCDA protocol, cross-reaction with non-mycobacteria and non-tuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) strains was not observed. Among clinically diagnosed TB patients, the sensitivity of liquid culture, Xpert MTB/RIF and multiplex MCDA assay was 42.0% (50/119), 49.6% (59/119), and 88.2% (105/119), respectively. Among culture positive samples, the sensitivity of Xpert MTB/RIF and multiplex MCDA assay was 86.0% (43/50) and 98.0% (49/50), respectively. Among culture negative samples, the sensitivity of Xpert MTB/RIF and multiplex MCDA assay was 23.2% (16/69) and 81.2% (56/69), respectively. The specificity was 100% (60/60) for Xpert MTB/RIF and 98.3% (59/60) for multiplex MCDA. Therefore, the multiplex MCDA assay for MTB detection is rapid, sensitive and easy to use and may be a promising test for early diagnosis of TB.
Keywords: MCDA-LFB; Mycobacterium tuberculosis; lateral flow biosensor; limit of detection; multiple cross displacement amplification.
Copyright © 2019 Jiao, Wang, Wang, Wang, Xiao, Sun, Li, Wen, Zhang, Ma, Huang and Shen.
Figures


References
-
- Chakravorty S., Simmons A. M., Rowneki M., Parmar H., Cao Y., Ryan J., et al. (2017). The new xpert MTB/RIF ultra: improving detection of mycobacterium tuberculosis and resistance to rifampin in an assay suitable for point-of-care testing. mBio 8 e812–e817. 10.1128/mBio.00812-17 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cronin W. A., Golub J. E., Magder L. S., Baruch N. G., Lathan M. J., Mukasa L. N., et al. (2001). Epidemiologic usefulness of spoligotyping for secondary typing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates with low copy numbers of IS6110. J. Clin. Microbiol. 39 3709–3711. 10.1128/JCM.39.10.3709-3711.2001 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dorman S. E., Schumacher S. G., Alland D., Nabeta P., Armstrong D. T., King B., et al. (2018). Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra for detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance: a prospective multicentre diagnostic accuracy study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 18 76–84. 10.1016/S1473-3099(17)30691-6 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

