Bacterial RNA Contributes to the Down-Modulation of MHC-II Expression on Monocytes/Macrophages Diminishing CD4+ T Cell Responses
- PMID: 31572389
- PMCID: PMC6753364
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02181
Bacterial RNA Contributes to the Down-Modulation of MHC-II Expression on Monocytes/Macrophages Diminishing CD4+ T Cell Responses
Abstract
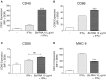
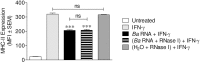
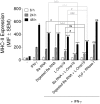
Brucella abortus, the causative agent of brucellosis, displays many resources to evade T cell responses conducive to persist inside the host. Our laboratory has previously showed that infection of human monocytes with B. abortus down-modulates the IFN-γ-induced MHC-II expression. Brucella outer membrane lipoproteins are structural components involved in this phenomenon. Moreover, IL-6 is the soluble factor that mediated MHC-II down-regulation. Yet, the MHC-II down-regulation exerted by lipoproteins was less marked than the one observed as consequence of infection. This led us to postulate that there should be other components associated with viable bacteria that may act together with lipoproteins in order to diminish MHC-II. Our group has recently demonstrated that B. abortus RNA (PAMP related to pathogens' viability or vita-PAMP) is involved in MHC-I down-regulation. Therefore, in this study we investigated if B. abortus RNA could be contributing to the down-regulation of MHC-II. This PAMP significantly down-modulated the IFN-γ-induced MHC-II surface expression on THP-1 cells as well as in primary human monocytes and murine bone marrow macrophages. The expression of other molecules up-regulated by IFN-γ (such as co-stimulatory molecules) was stimulated on monocytes treated with B. abortus RNA. This result shows that this PAMP does not alter all IFN-γ-induced molecules globally. We also showed that other bacterial and parasitic RNAs caused MHC-II surface expression down-modulation indicating that this phenomenon is not restricted to B. abortus. Moreover, completely degraded RNA was also able to reproduce the phenomenon. MHC-II down-regulation on monocytes treated with RNA and L-Omp19 (a prototypical lipoprotein of B. abortus) was more pronounced than in monocytes stimulated with both components separately. We also demonstrated that B. abortus RNA along with its lipoproteins decrease MHC-II surface expression predominantly by a mechanism of inhibition of MHC-II expression. Regarding the signaling pathway, we demonstrated that IL-6 is a soluble factor implicated in B. abortus RNA and lipoproteins-triggered MHC-II surface down-regulation. Finally, CD4+ T cells functionality was affected as macrophages treated with these components showed lower antigen presentation capacity. Therefore, B. abortus RNA and lipoproteins are two PAMPs that contribute to MHC-II down-regulation on monocytes/macrophages diminishing CD4+ T cell responses.
Keywords: Brucella abortus; MHC; antigen presentation/processing; bacterial RNA; monocytes/macrophages.
Copyright © 2019 Milillo, Trotta, Serafino, Marin Franco, Marinho, Alcain, Genoula, Balboa, Costa Oliveira, Giambartolomei and Barrionuevo.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

