Identifying the active components of Baihe-Zhimu decoction that ameliorate depressive disease by an effective integrated strategy: a systemic pharmacokinetics study combined with classical depression model tests
- PMID: 31572489
- PMCID: PMC6757420
- DOI: 10.1186/s13020-019-0254-9
Identifying the active components of Baihe-Zhimu decoction that ameliorate depressive disease by an effective integrated strategy: a systemic pharmacokinetics study combined with classical depression model tests
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Identifying the active components of Baihe-Zhimu decoction that ameliorate depressive disease by an effective integrated strategy: a systemic pharmacokinetics study combined with classical depression model tests.Chin Med. 2020 Apr 2;15:32. doi: 10.1186/s13020-020-00312-2. eCollection 2020. Chin Med. 2020. PMID: 32266001 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Modern pharmacological studies have demonstrated that Baihe-Zhimu decoction (BZD) has antidepressant effects. However, the complex composition and lack of clear evaluation standards for BZD make it less likely to be understood and accepted than evidence-based active natural compounds.
Methods: In this study, an effective method for the identification of antidepressant components was demonstrated and applied to BZD. The first step was to evaluate the efficacy of BZD by the forced swimming test (FST) and the tail suspension test (TST), followed by successive quantitative analyses of the absorbed constituents at different stages, such as before hepatic disposition, liver distribution, after hepatic disposition and brain distribution after the oral administration of BZD. Finally, the compounds detected in the brain were confirmed by activity testing.
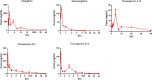
Results: Our investigation observed that timosaponin BII and timosaponin BIII were accurately determined in the brain after oral administration of BZD, and they were further confirmed to reduce the immobility time in the FST and TST. As described above, timosaponin BII and timosaponin BIII were used to scientifically and reasonably explain the effective chemical basis of the effect of BZD on depression.
Conclusions: This research affords an effective method to discover lead molecules for antidepressants from traditional Chinese medicine.
Keywords: Antidepressant; Baihe–Zhimu decoction; Drug discovery; Timosaponin BII; Timosaponin BIII.
© The Author(s) 2019.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Zhang NT, Cheng C, Olaleye OE, Sun Y, Li L, Huang YH, Du FF, Yang JL, Wang FQ, Shi YH, Xu F, Li YF, Wen Q, Zhang NX, Li C. Pharmacokinetics-based identification of potential therapeutic phthalides from XueBiJing, a chinese herbal injection used in sepsis management. Drug Metab Dispos. 2018;46(6):823–834. doi: 10.1124/dmd.117.079673. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

