Gene delivery into hepatic cells with ternary complexes of plasmid DNA, cationic liposomes and apolipoprotein E-derived peptide
- PMID: 31572511
- PMCID: PMC6755467
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2019.7863
Gene delivery into hepatic cells with ternary complexes of plasmid DNA, cationic liposomes and apolipoprotein E-derived peptide
Abstract
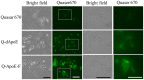
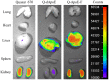
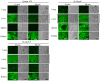
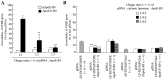
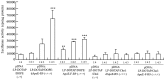
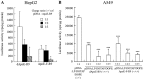
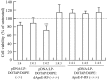
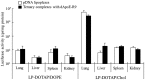
Cationic liposomes containing a cationic lipid, such as 1,2-dioleoyl-3-trimethylammonium-propane (DOTAP), have often been used for the transduction of plasmid DNA (pDNA) in vivo. However, such liposomes induce gene expression primarily in the lungs after intravenous injection. To improve the delivery of cationic liposomes/pDNA complexes (pDNA lipoplexes) to the liver by intravenous administration, the current study synthesized two apolipoprotein E (ApoE)-derived peptides, dApoE-R9 and ApoE-F-R9, for liver targeting via certain ApoE receptors, including the low-density lipoprotein receptor. Ternary complexes of pDNA, cationic liposomes and ApoE-R9 peptide were also prepared. After in vitro transfection, ternary complexes with DOTAP/1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine (DOPE) liposomes exhibited high transfection activity in HepG2 cells compared with DOTAP/cholesterol (Chol) liposomes. In particular, ternary complexes with dApoE-R9 exhibited high transfection activity in cells compared with ApoE-F-R9. However, in vivo transfection studies revealed that ternary complexes with DOTAP/DOPE liposomes and dApoE-R9 did not increase gene expression in the liver compared with DOTAP/DOPE lipoplexes. In contrast, ternary complexes with DOTAP/Chol liposomes and dApoE-R9 increased gene expression in the liver compared with DOTAP/Chol lipoplexes. The results demonstrated that the in vivo optimal liposomal formulation in ternary complexes with ApoE-R9 peptide for liver delivery were different from those that were in vitro.
Keywords: apolipoprotein E; cationic liposome; liver-targeting; plasmid DNA.
Copyright: © Hattori et al.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
