The regulation of oocyte maturation and ovulation in the closest sister group of vertebrates
- PMID: 31573508
- PMCID: PMC6786877
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.49062
The regulation of oocyte maturation and ovulation in the closest sister group of vertebrates
Abstract
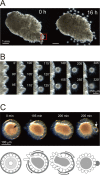
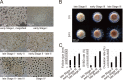
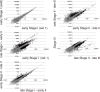
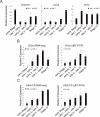
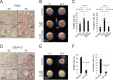
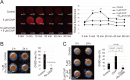
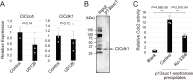
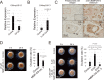
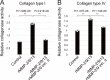
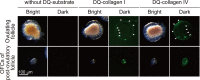
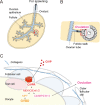
Ascidians are the closest living relatives of vertebrates, and their study is important for understanding the evolutionary processes of oocyte maturation and ovulation. In this study, we first examined the ovulation of Ciona intestinalis Type A by monitoring follicle rupture in vitro, identifying a novel mechanism of neuropeptidergic regulation of oocyte maturation and ovulation. Ciona vasopressin family peptide (CiVP) directly upregulated the phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (CiErk1/2) via its receptor. CiVP ultimately activated a maturation-promoting factor, leading to oocyte maturation via germinal vesicle breakdown. CiErk1/2 also induced expression of matrix metalloproteinase (CiMMP2/9/13) in the oocyte, resulting in collagen degradation in the outer follicular cell layer and liberation of fertile oocytes from the ovary. This is the first demonstration of essential pathways regulating oocyte maturation and ovulation in ascidians and will facilitate investigations of the evolutionary process of peptidergic regulation of oocyte maturation and ovulation throughout the phylum Chordata.
Keywords: C. intestinalis; cell biology; evolutionary biology; follicle; maturation; ovulation; vasopressin.
© 2019, Matsubara et al.
Conflict of interest statement
SM, AS, TO, TK, HS No competing interests declared
Figures


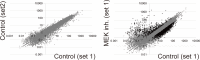



References
-
- Aoyama M, Kawada T, Fujie M, Hotta K, Sakai T, Sekiguchi T, Oka K, Satoh N, Satake H. A novel biological role of tachykinins as an up-regulator of oocyte growth: identification of an evolutionary origin of tachykininergic functions in the ovary of the ascidian, Ciona intestinalis. Endocrinology. 2008;149:4346–4356. doi: 10.1210/en.2008-0323. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Brunetti R, Gissi C, Pennati R, Caicci F, Gasparini F, Manni L. Morphological evidence that the molecularly determined Ciona intestinalis type A and type B are different species: Ciona robusta and Ciona intestinalis. Journal of Zoological Systematics and Evolutionary Research. 2015;53:186–193. doi: 10.1111/jzs.12101. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

