Sustained delivery of olanzapine from sunflower oil-based polyol-urethane nanoparticles synthesised through a cyclic carbonate ring-opening reaction
- PMID: 31573539
- PMCID: PMC8676627
- DOI: 10.1049/iet-nbt.2018.5440
Sustained delivery of olanzapine from sunflower oil-based polyol-urethane nanoparticles synthesised through a cyclic carbonate ring-opening reaction
Abstract
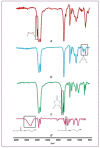
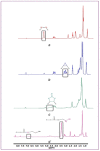
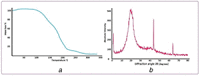
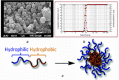
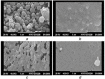
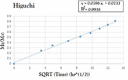
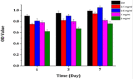
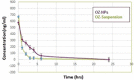
The forefront horizon of biomedical investigations in recent decades is parcelling-up and delivery of drugs to achieve controlled/targeted release. In this regard, developing green-based delivery systems for a spatiotemporal controlling therapeutic agent have drawn a lot of attention. A facile route based on cyclic carbonate ring-opening reaction has been utilised to synthesise a bio-based polyol-containing urethane bond [polyol-urethane (POU)] as a nanoparticulate drug delivery system of olanzapine in order to enhance its bioavailability. After characterisation, the nanoparticles were also estimated for in vitro release, toxicity, and pharmacokinetic studies. As olanzapine has shown poor bioavailability and permeability in the brain, the sustained release of olanzapine from the designed carriers could enhance pharmacokinetic effectiveness. POU in the aqueous solution formed micelles with a hydrophobic core and embedded olanzapine under the influence of its hydrophobic nature. Drug release from the nanoparticles (90 ± 0.43 nm in diameter) indicated a specific pattern with initial burst release, and then a sustained release behaviour (82 ± 3% after 168 h), by the Higuchi-based release mechanism. Pharmacokinetics assessments of POU-olanzapine nanoparticles were carried in male Wistar rats through intravenous administration. The obtained results paved a way to introduce the POU as an efficient platform to enhance the bioavailability of olanzapine in therapeutic methods.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Design, characterization and in vitro evaluation of novel amphiphilic block sunflower oil-based polyol nanocarrier as a potential delivery system: Raloxifene-hydrochloride as a model.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017 Sep 1;78:59-68. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2017.03.235. Epub 2017 Mar 27. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017. PMID: 28576026
-
Design and in vivo evaluation of solid lipid nanoparticulate systems of Olanzapine for acute phase schizophrenia treatment: Investigations on antipsychotic potential and adverse effects.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2017 Jun 15;104:315-325. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2017.03.050. Epub 2017 Apr 11. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2017. PMID: 28408348
-
Brain targeting of olanzapine via intranasal delivery of core-shell difunctional block copolymer mixed nanomicellar carriers: in vitro characterization, ex vivo estimation of nasal toxicity and in vivo biodistribution studies.Int J Pharm. 2013 Aug 16;452(1-2):300-10. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2013.04.084. Epub 2013 May 14. Int J Pharm. 2013. PMID: 23684658
-
Hydrophilic Polymers for Modified-Release Nanoparticles: A Review of Mathematical Modelling for Pharmacokinetic Analysis.Curr Pharm Des. 2015;21(22):3090-6. doi: 10.2174/1381612821666150531163617. Curr Pharm Des. 2015. PMID: 26027576 Review.
-
Polymeric nanoparticles as carrier for targeted and controlled delivery of anticancer agents.Ther Deliv. 2019 Aug;10(8):527-550. doi: 10.4155/tde-2019-0044. Epub 2019 Sep 9. Ther Deliv. 2019. PMID: 31496433 Review.
Cited by
-
Electrically Conductive Materials: Opportunities and Challenges in Tissue Engineering.Biomolecules. 2019 Sep 4;9(9):448. doi: 10.3390/biom9090448. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31487913 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development and Utilization of Multifunctional Polymeric Scaffolds for the Regulation of Physical Cellular Microenvironments.Polymers (Basel). 2021 Nov 10;13(22):3880. doi: 10.3390/polym13223880. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34833179 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Boron Nitride Nanotube as an Antimicrobial Peptide Carrier: A Theoretical Insight.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Mar 4;16:1837-1847. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S298699. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 33692624 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetics and Optimization Studies of Controlled 5-Fluorouracil Release from Graphene Oxide Incorporated Vegetable Oil-Based Polyurethane Composite Film.ACS Omega. 2024 Nov 18;9(48):47395-47409. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c02247. eCollection 2024 Dec 3. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 39651068 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hafshejani T.M. Zamanian A. Venugopal J.R. et al.: ‘Antibacterial glass‐ionomer cement restorative materials: a critical review on the current status of extended release formulations’, J. Control. Release, 2017, 262, pp. 317 –328 - PubMed
-
- Mohebbi S. Nezhad M.N. Zarrintaj P. et al.: ‘Chitosan in biomedical engineering: a critical review’, Curr. Stem Cell Res. Ther., 2019, 14, pp. 93 –116 - PubMed
-
- Dai L. Liu K. Si C. et al.: ‘Ginsenoside nanoparticle: a new green drug delivery system’, J. Mater. Chem. B, 2016, 4, pp. 529 –538 - PubMed
-
- Bakhshandeh B. Zarrintaj P. Oftadeh M.O. et al.: ‘Tissue engineering; strategies, tissues, and biomaterials’, Biotechnol. Genet. Eng. Rev., 2017, 33, pp. 144 –172 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

