Feasibility and Validity of Geographically Explicit Ecological Momentary Assessment With Recall-Aided Space-Time Budgets
- PMID: 31573764
- PMCID: PMC6774631
- DOI: 10.1111/jora.12474
Feasibility and Validity of Geographically Explicit Ecological Momentary Assessment With Recall-Aided Space-Time Budgets
Abstract
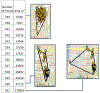
We employ data from the Adolescent Health and Development in Context Study-a representative sample of urban youth ages 11-17 in and around the Columbus, OH area-to investigate the feasibility and validity of smartphone-based geographically explicit ecological momentary assessment (GEMA). Age, race, household income, familiarity with smartphones, and self-control were associated with missing global positioning systems (GPS) coverage, whereas school day was associated with discordance between percent of time at home based on GPS-only versus recall-aided space-time budget data. Fatigue from protocol compliance increases missing GPS across the week, which results in more discordance. Although some systematic differences were observed, these findings offer evidence that smartphone-based GEMA is a viable method for the collection of activity space data on urban youth.
© 2018 Society for Research on Adolescence.
Figures


References
-
- Anderson J (1971). Space-time budgets and activity studies in urban geography and planning. Environment and Planning A, 3(4), 353–368. 10.1068/a030353 - DOI
-
- Auld J, & Mohammadian A (2014). Collecting Activity-Travel and Planning Process Data Using GPS-Based Prompted Recall Surveys: Recent Experience and Future Directions. Hersey: Igi Global.
-
- Auld J, Williams C, Mohammadian A, & Nelson P (2009). An automated GPS-based prompted recall survey with learning algorithms. Transportation Letters, 1(1), 59–79. 10.3328/TL.2009.01.01.59-79 - DOI
-
- Bricka SG, Sen S, Paleti R, & Bhat CR (2012). An analysis of the factors influencing differences in survey-reported and GPS-recorded trips. Transportation Research Part C-Emerging Technologies, 21(1), 67–88. 10.1016/j.trc.2011.09.005 - DOI
-
- Browning CR, Cagney KA, & Boettner B (2016). Neighborhoods, activity spaces, and the life course In Shanahan MJ, Mortimer JT, & Johnson MK (Eds.), Handbook of the Life Course (Vol. II, pp. 597–620). New York, NY: Springer; Retrieved from http://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-319-20880-0_26/fulltext.html - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
