Reduction of intra-abdominal pain through transcranial direct current stimulation: A systematic review
- PMID: 31574799
- PMCID: PMC6775377
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000017017
Reduction of intra-abdominal pain through transcranial direct current stimulation: A systematic review
Abstract
Background: Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) is a non-invasive brain stimulation technique to modulate cortical excitability and to induce neuronal plasticity. With a wide range of applications in neurological and psychiatric disorders, the efficiency of tDCS is also studied in the treatment of various pain conditions. Treatment with tDCS might accordingly provide pain relief for patients with acute or chronic pain and thus lead to an increase in quality of life. Moreover, applied as an adjunct therapy, tDCS can reduce help to reduce pain medication intake and accompanying adverse events. To this end, this review examines studies evaluating the efficacy of tDCS in pain relief in patients with intra-abdominal pain.
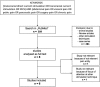
Methods: A structured search of the PubMed medical database was carried out to identify possibly relevant studies. Studies were compared in terms of treatment characteristics, general conditions, and results. Jadad scale was applied for quality analyses.
Results: Out of 289 articles that were found initially, 6 studies were identified that met eligibility criteria. Five out of 6 studies reported significant effects for pain reduction in different types of intra-abdominal pain.
Conclusions: Results indicate that tDCS might be able to reduce intra-abdominal pain. However, more randomized-controlled trials with larger sample size are necessary to define clinically relevant effects as well as treatment characteristics such as duration of stimulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Wagner T, Valero-Cabre A, Pascual-Leone A. Noninvasive human brain stimulation. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 2007;9:527–65. - PubMed
-
- Nitsche MA, Paulus W. Sustained excitability elevations induced by transcranial DC motor cortex stimulation in humans. Neurology 2001;57:1899–901. - PubMed
-
- Nitsche MA, Cohen LG, Wassermann EM, et al. Transcranial direct current stimulation: State of the art 2008. Brain Stimul 2008;1:206–23. - PubMed
-
- Purpura DP, McMurtry JG. Intracellular activities and evoked potential changes during polarization of motor cortex. J Neurophysiol 1965;28:166–85. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

