The efficacy and safety of irinotecan ± bevacizumab compared with oxaliplatin ± bevacizumab for metastatic colorectal cancer: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 31574891
- PMCID: PMC6775432
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000017384
The efficacy and safety of irinotecan ± bevacizumab compared with oxaliplatin ± bevacizumab for metastatic colorectal cancer: A meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Irinotecan (IRI)-based and oxaliplatin (OXA)-based regimens are available for the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC). Several studies have published inconsistent results in their comparisons of the efficacy and toxicity of IRI ± bevacizumab and OXA ± bevacizumab. This meta-analysis was performed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of these 2 regimens in patients with mCRC.
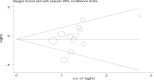
Methods: We searched several databases to identify relevant studies, including PubMed, EMBASE, and the Cochrane Controlled Trials Register. The primary endpoints were overall survival (OS) and time to progression (TTP). The secondary comparisons were overall response rate (ORR) and toxicity. In addition, the hazard ratio (HR) or risk ratio (RR) values with their corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were extracted from these studies.
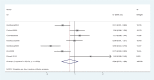
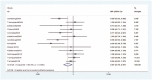
Results: Pooled data of 13 studies demonstrated no significant differences in OS (HR = 0.96, 95% CI: 0.86-1.08, P = .53) and TTP (HR = 0.88, 95% CI: 0.72-1.08, P = .24) between the 2 groups. However, the ORR (RR = 0.87, 95% CI: 0.78-0.97, P = .02) was clearly improved in the OXA ± bevacizumab arm. Higher incidences of grade 3/4 nausea (RR = 1.63, 95% CI: 1.28-2.07, P < .001), vomiting (RR = 1.40, 95% CI: 1.09-1.81, P = .01), diarrhea (RR = 1.44, 95% CI: 1.23-1.70, P < .001), and anemia (RR = 4.13, 95% CI: 2.75-6.22, P < .001) were observed in the IRI group. However, the incidences of grade 3/4 neutropenia (RR = 0.75, 95% CI: 0.68-0.83, P < .001), thrombocytopenia (RR = 0.43, 95% CI: 0.26-0.73, P = .002), and paresthesia/neurological disturbances (RR = 0.04, 95% CI: 0.02-0.07, P < .001) were higher in the OXA group.
Conclusion: This meta-analysis confirmed that the OXA ± bevacizumab regimen as a maintenance therapy significantly improved the ORR in patients with mCRC. Exhibiting strong efficacy and safety, the OXA and OXA plus bevacizumab regimens are preferred as first-line treatments for mCRC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparison of irinotecan and oxaliplatin as the first-line therapies for metastatic colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis.BMC Cancer. 2021 Feb 4;21(1):116. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-07823-7. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33541293 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of the addition of bevacizumab, oxaliplatin, or irinotecan to fluoropyrimidin in the first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer in elderly patients.Int J Colorectal Dis. 2018 Aug;33(8):1125-1130. doi: 10.1007/s00384-018-3053-3. Epub 2018 Apr 21. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2018. PMID: 29680896
-
Effect of Bevacizumab in Combination With Standard Oxaliplatin-Based Regimens in Patients With Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Randomized Clinical Trial.JAMA Netw Open. 2021 Jul 1;4(7):e2118475. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.18475. JAMA Netw Open. 2021. PMID: 34309665 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Does the Chemotherapy Backbone Impact on the Efficacy of Targeted Agents in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Literature.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 14;10(8):e0135599. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0135599. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26275292 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Bevacizumab Plus Oxaliplatin- or Irinotecan-Based Doublet Backbone Chemotherapy as the First-Line Treatment of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Drug Saf. 2021 Jan;44(1):29-40. doi: 10.1007/s40264-020-00997-2. Epub 2020 Nov 12. Drug Saf. 2021. PMID: 33180265
Cited by
-
Application of IVIM-DWI in Detecting the Tumor Vasculogenic Mimicry Under Antiangiogenesis Combined With Oxaliplatin Treatment.Front Oncol. 2020 Aug 18;10:1376. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01376. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32974136 Free PMC article.
-
Irinotecan and its metabolite SN38 inhibits procollagen I production of dermal fibroblasts from Systemic Sclerosis patients.Sci Rep. 2021 Sep 9;11(1):18011. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-97538-3. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34504265 Free PMC article.
-
Drug-Drug Interactions of Irinotecan, 5-Fluorouracil, Folinic Acid and Oxaliplatin and Its Activity in Colorectal Carcinoma Treatment.Molecules. 2020 Jun 4;25(11):2614. doi: 10.3390/molecules25112614. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32512790 Free PMC article.
-
An overview and bibliometric analysis on the colorectal cancer therapy by magnetic functionalized nanoparticles for the responsive and targeted drug delivery.J Nanobiotechnology. 2021 Nov 29;19(1):399. doi: 10.1186/s12951-021-01150-6. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021. PMID: 34844632 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Fedewa SA, Miller KD, et al. Cancer statistics for Hispanics/Latinos, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin 2015;65:457–80. - PubMed
-
- Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin 2016;66:115–32. - PubMed
-
- Bekaii-Saab T, Wu C. Seeing the forest through the trees: a systematic review of the safety and efficacy of combination chemotherapies used in the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 2014;91:9–34. - PubMed
-
- Van Cutsem E, Cunningham D, Ten Bokkel Huinink WW, et al. Clinical activity and benefit of irinotecan (CPT-11) in patients with colorectal cancer truly resistant to 5-fluorouracil (5-FU). Eur J Cancer 1999;35:54–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

