Enjoyment and Intensity of Physical Activity in Immersive Virtual Reality Performed on Innovative Training Devices in Compliance with Recommendations for Health
- PMID: 31574911
- PMCID: PMC6801661
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph16193673
Enjoyment and Intensity of Physical Activity in Immersive Virtual Reality Performed on Innovative Training Devices in Compliance with Recommendations for Health
Abstract
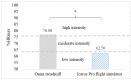
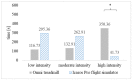
The aim of the study is to assess the enjoyment and intensity of physical exercise while practicing physical activity (PA) in immersive virtual reality (IVR) using innovative training devices (omni-directional Omni treadmill and Icaros Pro flight simulator). The study also contains the results of subjective research on the usefulness of such a form of PA in the opinion of users. In total, 61 adults (10 women and 51 men) took part in the study. To assess the enjoyment level (EL) Interest/Enjoyment subscale of Intrinsic Motivation Inventory (IMI) was used. Exercise intensity was assessed during 10-min sessions of active video games (AVGs) in IVR based on heart rate (HR). The average enjoyment level during physical exercise in IVR on the tested training devices was high (Omni 5.74 points, Icaros 5.60 points on a 1-7 Likert scale) and differed significantly in favor of PA on Omni. In the opinion of the majority of participants, AVGs in IVR on the tested devices constitute a sufficiently useful form of PA to meet the needs of leisure time activities, and they can even replace some forms of physical effort performed in a classic way. The intensity of PA during games on training devices was at the level recommended for health benefits for 80.55% (Omni) and 50.77% (Icaros Pro) of its duration. Based on the conducted research, it can be assumed that AVGs in IVR using a multi-directional treadmill and a flight simulator can be an effective tool for increasing participation in health-oriented PA.
Keywords: health-oriented physical activity; immersive virtual reality; intensity of physical activity; virtual reality.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Recreational cycling provides greater satisfaction and flow in an immersive virtual environment than in real life.BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2024 Jan 30;16(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s13102-024-00818-4. BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2024. PMID: 38291484 Free PMC article.
-
Can Physical Activity in Immersive Virtual Reality Be Attractive and Have Sufficient Intensity to Meet Health Recommendations for Obese Children? A Pilot Study.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Nov 1;17(21):8051. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17218051. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 33139604 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Elastic Resistance on Exercise Intensity and User Satisfaction While Playing the Active Video Game BoxVR in Immersive Virtual Reality: Empirical Study.JMIR Serious Games. 2024 Jul 16;12:e58411. doi: 10.2196/58411. JMIR Serious Games. 2024. PMID: 39030677 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing Physical Activity with Immersive Virtual Reality: A Systematic Review.Cyberpsychol Behav Soc Netw. 2024 May;27(5):303-317. doi: 10.1089/cyber.2023.0394. Epub 2024 Mar 20. Cyberpsychol Behav Soc Netw. 2024. PMID: 38506442
-
Virtual-reality exergaming improves performance during high-intensity interval training.Eur J Sport Sci. 2019 Jul;19(6):719-727. doi: 10.1080/17461391.2018.1542459. Epub 2018 Nov 7. Eur J Sport Sci. 2019. PMID: 30403927 Review.
Cited by
-
Virtual reality applications for rehabilitation of COVID-19 patients: A systematic review.Health Sci Rep. 2022 Oct 3;5(6):e853. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.853. eCollection 2022 Nov. Health Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36210874 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic cost and mechanical work of walking in a virtual reality emulator.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2024 Mar;124(3):783-792. doi: 10.1007/s00421-023-05306-0. Epub 2023 Sep 30. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2024. PMID: 37776345 Free PMC article.
-
Physical Activity in Immersive Virtual Reality: A Scoping Review.Healthcare (Basel). 2023 May 25;11(11):1553. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11111553. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37297694 Free PMC article.
-
Active video games in fully immersive virtual reality elicit moderate-to-vigorous physical activity and improve cognitive performance in sedentary college students.J Sport Health Sci. 2022 Mar;11(2):164-171. doi: 10.1016/j.jshs.2021.05.002. Epub 2021 May 16. J Sport Health Sci. 2022. PMID: 34004390 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Recreational cycling provides greater satisfaction and flow in an immersive virtual environment than in real life.BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2024 Jan 30;16(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s13102-024-00818-4. BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2024. PMID: 38291484 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO . World Health Statistics 2018: Monitoring Health for the SDGs. WHO; Geneva, Switzerland: 2018.
-
- Ramón J.C., Verdaguer F.J.P., Conti J.V., Rotger P.A.B., Sampol P.P. Adolescence, physical inactivity and overweight: Analysis based on socio-personal variables of the parens and the type of sport practiced by the children. RETOS. 2015;21:5–8.
-
- Carvalho B., Soares M., Neves A., Soares G., Lins A. Ergonomics in Design: Methods and Techniques. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 2016. Virtual reality devices applied to digital games. A literature review; pp. 125–136.
-
- Van Dam A., Laidlaw D.H., Simpson R.M. Experiments in Immersive Virtual Reality for Scientific Visualization. Comput. Graph. 2002;26:535–555. doi: 10.1016/S0097-8493(02)00113-9. - DOI
-
- Southgate E., Smith S.P., Cividino C., Saxby S., Kilham J., Eather G., Scevak J., Summerville D., Buchanan R., Bergin C. Embedding immersive virtual reality in classrooms: Ethical, organisational and educational lessons in bridging research and practice. Int. J. Child Comput. Interact. 2019;19:19–29. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcci.2018.10.002. - DOI

