Histological Change in Soft Tissue Surrounding Titanium Plates after Jaw Surgery
- PMID: 31574920
- PMCID: PMC6804085
- DOI: 10.3390/ma12193205
Histological Change in Soft Tissue Surrounding Titanium Plates after Jaw Surgery
Abstract
The aim of this study was to evaluate the microscopic structure of soft tissue covering titanium plates and screws used in jaw surgery (mandible fracture and orthognathic surgery), after a minimum period of 12 months from insertion, and to quantify the presence of any metallic particles. Periosteum covering the osteosynthesis plates was removed from 20 patients and examined by light microscopy in order to assess the cell morphological changes and the possibility of metal particles presence in the soft tissue. Local signs of tissue toxicity or inflammation were taken into consideration when evaluating the routine removal of titanium maxillofacial miniplates. No signs of screw loosening or acute inflammation were detected on the osteosynthesis site, but de-coloration of the periosteum was seen, and metallic particles were observed to have migrated into the soft tissues. Even if the titanium is well-tolerated by the human body in time, without severe local or general complications, our findings suggest that plate removal should be considered after bone healing has occurred.
Keywords: Ti particles; implants; miniplates; osteosynthesis; titanium.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


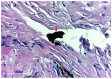
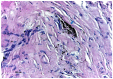
Similar articles
-
Dynamic study about metal release from titanium miniplates in maxillofacial surgery.Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2001 Jun;30(3):185-8. doi: 10.1054/ijom.2000.0039. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2001. PMID: 11420898
-
The fate of titanium miniplates and screws used in maxillofacial surgery: a 10 year retrospective study.Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009 Jul;38(7):731-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2009.02.016. Epub 2009 Mar 21. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009. PMID: 19303742
-
Tissue response to titanium plates: a transmitted electron microscopic study.J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1997 Apr;55(4):322-6. doi: 10.1016/s0278-2391(97)90115-4. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1997. PMID: 9120693
-
Titanium plate removal in orthognathic surgery: prevalence, causes and risk factors. A systematic literature review and meta-analysis.Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2020 Jun;49(6):770-778. doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2019.11.003. Epub 2019 Nov 28. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2020. PMID: 31786103
-
Tissue response to titanium implant using scanning electron microscope.Natl J Maxillofac Surg. 2013 Jan;4(1):7-12. doi: 10.4103/0975-5950.117815. Natl J Maxillofac Surg. 2013. PMID: 24163546 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Titanium or Biodegradable Osteosynthesis in Maxillofacial Surgery? In Vitro and In Vivo Performances.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Jul 7;14(14):2782. doi: 10.3390/polym14142782. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35890557 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Risk Factors Contributing to Symptomatic Miniplate Removal following Orthognathic Surgery: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Clin Med. 2024 Jun 5;13(11):3335. doi: 10.3390/jcm13113335. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38893045 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of the Mandibular Condyle Morphologic Relation before and after Orthognathic Surgery in Class II and III Malocclusion Patients Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography.Biology (Basel). 2022 Sep 14;11(9):1353. doi: 10.3390/biology11091353. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36138832 Free PMC article.
-
Rigid versus Resorbable Plate Fixation in Fronto-Orbital Advancement in Unicoronal Stenosis - A Retrospective Study.Ann Maxillofac Surg. 2022 Jan-Jun;12(1):22-26. doi: 10.4103/ams.ams_35_22. Epub 2022 Aug 16. Ann Maxillofac Surg. 2022. PMID: 36199468 Free PMC article.
-
In Silico Biomechanical Evaluation of WE43 Magnesium Plates for Mandibular Fracture Fixation.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Feb 10;9:803103. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.803103. eCollection 2021. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35223813 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Souza J.C.M., Tajiri H.A., Morsch C.S., Buciumeanu M., Mathew M.T., Silva F.S., Henriques B. Tribocorrosion Behavior of Ti6Al4V Coated with a Bio-absorbable Polymer for Biomedical Applications. J. Bio- Tribo-Corros. 2015;1:27. doi: 10.1007/s40735-015-0029-5. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

