Does Sarcopenia Increase the Risk for Fresh Vertebral Fragility Fractures?: A Case-Control Study
- PMID: 31575110
- PMCID: PMC7010510
- DOI: 10.31616/asj.2019.0049
Does Sarcopenia Increase the Risk for Fresh Vertebral Fragility Fractures?: A Case-Control Study
Abstract
Study design: Case-control study.
Purpose: Sarcopenia is an age associated condition characterized by decrease in muscle mass, strength, and physical performance. We aimed to investigate whether sarcopenia increased the risk of vertebral fragility fractures among the elderly.
Overview of literature: Initial reports on sarcopenia suggest its contribution to the development of vertebral fragility fractures. However, recent studies showed contradictory findings.
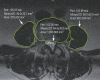
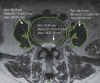
Methods: Fifty-one consecutive patients with vertebral fragility fractures and matched controls without fractures were evaluated for sarcopenia, T-score, body mass index, and presence of preexisting vertebral fractures. Sarcopenia was diagnosed as total psoas cross-sectional area (TPA) 2 standard deviations below normative value from normal young adults and decreased handgrip strength (26 kg for men and 18 kg for women). Univariate and multivariate analyses were performed using the fresh fracture occurrence as the dependent variable.
Results: Sarcopenia was confirmed in 29.4% and 7.8% of cases and controls (p=0.005), respectively; 56.8% and 13.7% of cases and controls had previous vertebral fractures. Sarcopenia prevalence was greater among those with previous fractures (38% vs. 7.6%; odds ratio, 7.76; p<0.001). TPA was lower among the cases (1,278 mm2 vs. 1,569 mm2 , p=0.001) and those with previous fractures (1,168 mm2 vs. 1,563 mm2 , p<0.001). Handgrip strength was greater among those without previous fractures (19.6 kg vs. 16.3 kg, p=0.05). In multivariate analysis, sarcopenia was not identified as a significant predictor of fresh fractures whereas previous fractures and lower T-score were found to be significant.
Conclusions: Sarcopenia is not an independent risk factor for fresh vertebral fragility fractures in the elderly.
Keywords: Muscle strength; Osteoporosis; Osteoporotic fractures; Sarcopenia; Skeletal muscle.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
-
- Center JR, Nguyen TV, Schneider D, Sambrook PN, Eisman JA. Mortality after all major types of osteoporotic fracture in men and women: an observational study. Lancet. 1999;353:878–82. - PubMed
-
- Kado DM, Browner WS, Palermo L, Nevitt MC, Genant HK, Cummings SR. Vertebral fractures and mortality in older women: a prospective study: study of Osteoporotic Fractures Research Group. Arch Intern Med. 1999;159:1215–20. - PubMed
-
- Tagliaferri C, Wittrant Y, Davicco MJ, Walrand S, Coxam V. Muscle and bone, two interconnected tissues. Ageing Res Rev. 2015;21:55–70. - PubMed
-
- Tarantino U, Piccirilli E, Fantini M, Baldi J, Gasbarra E, Bei R. Sarcopenia and fragility fractures: molecular and clinical evidence of the bone-muscle interaction. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;97:429–37. - PubMed
-
- Ho-Pham LT, Nguyen UD, Nguyen TV. Association between lean mass, fat mass, and bone mineral density: a meta-analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99:30–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

