Load-dependent adaptation near zero load in the bacterial flagellar motor
- PMID: 31575345
- PMCID: PMC6833329
- DOI: 10.1098/rsif.2019.0300
Load-dependent adaptation near zero load in the bacterial flagellar motor
Abstract
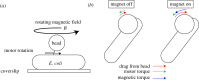
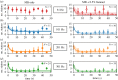
The bacterial flagellar motor is an ion-powered transmembrane protein complex which drives swimming in many bacterial species. The motor consists of a cytoplasmic 'rotor' ring and a number of 'stator' units, which are bound to the cell wall of the bacterium. Recently, it has been shown that the number of functional torque-generating stator units in the motor depends on the external load, and suggested that mechanosensing in the flagellar motor is driven via a 'catch bond' mechanism in the motor's stator units. We present a method that allows us to measure-on a single motor-stator unit dynamics across a large range of external loads, including near the zero-torque limit. By attaching superparamagnetic beads to the flagellar hook, we can control the motor's speed via a rotating magnetic field. We manipulate the motor to four different speed levels in two different ion-motive force (IMF) conditions. This framework allows for a deeper exploration into the mechanism behind load-dependent remodelling by separating out motor properties, such as rotation speed and energy availability in the form of IMF, that affect the motor torque.
Keywords: bacterial flagellar motor; mechanobiology; molecular motors.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare we have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effect of the MotA(M206I) Mutation on Torque Generation and Stator Assembly in the Salmonella H+-Driven Flagellar Motor.J Bacteriol. 2019 Feb 25;201(6):e00727-18. doi: 10.1128/JB.00727-18. Print 2019 Mar 15. J Bacteriol. 2019. PMID: 30642987 Free PMC article.
-
A Chaperone for the Stator Units of a Bacterial Flagellum.mBio. 2019 Aug 6;10(4):e01732-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01732-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 31387912 Free PMC article.
-
Direct observation of speed fluctuations of flagellar motor rotation at extremely low load close to zero.Mol Microbiol. 2020 Apr;113(4):755-765. doi: 10.1111/mmi.14440. Epub 2019 Dec 27. Mol Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 31828860
-
Structure and Dynamics of the Bacterial Flagellar Motor Complex.Biomolecules. 2024 Nov 22;14(12):1488. doi: 10.3390/biom14121488. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39766194 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Architecture and Assembly of the Bacterial Flagellar Motor Complex.Subcell Biochem. 2021;96:297-321. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-58971-4_8. Subcell Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33252734 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanosensitive remodeling of the bacterial flagellar motor is independent of direction of rotation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Apr 13;118(15):e2024608118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2024608118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 33876769 Free PMC article.
-
Relaxation time asymmetry in stator dynamics of the bacterial flagellar motor.Sci Adv. 2022 Mar 25;8(12):eabl8112. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abl8112. Epub 2022 Mar 23. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 35319986 Free PMC article.
-
ATP synthase: Evolution, energetics, and membrane interactions.J Gen Physiol. 2020 Nov 2;152(11):e201912475. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201912475. J Gen Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32966553 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bacterial motility: machinery and mechanisms.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2022 Mar;20(3):161-173. doi: 10.1038/s41579-021-00626-4. Epub 2021 Sep 21. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 34548639 Review.
-
Physical mechanism reveals bacterial slowdown above a critical number of flagella.J R Soc Interface. 2024 Nov;21(220):20240283. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2024.0283. Epub 2024 Nov 6. J R Soc Interface. 2024. PMID: 39503268 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nirody JA, Sun Y-R, Lo C-J. 2017. The biophysicist’s guide to the bacterial flagellar motor. Adv. Phys.: X 2, 324–343. (10.1080/23746149.2017.1289120) - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

